Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
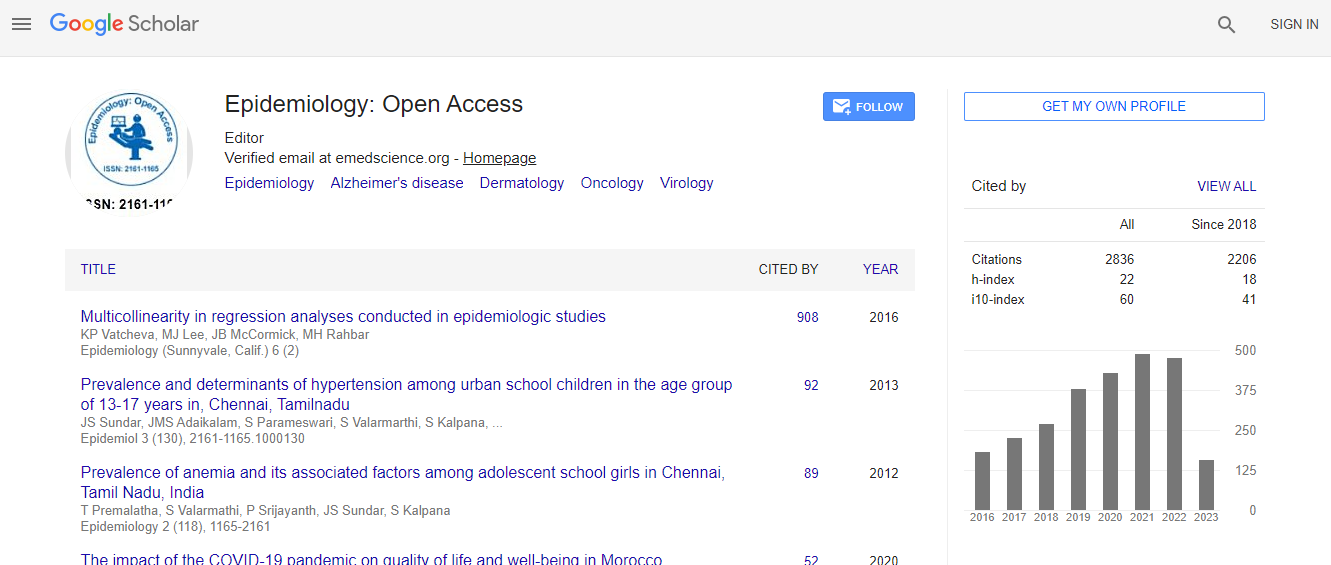
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 2820
Epidemiology: Open Access received 2820 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Molecular epidemiology and genetic analysis of H9N2 avian influenza viruses comparing with highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses in Korea
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Jin-Wook Jang1, Il-Hwan Kim2, Chung-Yong Lee1, Hyuk-Joon Kwon1 and Jae-Hong Kim1
Posters-Accepted Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
H9N2 avian influenza viruses (AIVs) have become endemic and circulated in poultry industries in Korea since the first
outbreak in 1996. We surveyed H9N2 AIVs in Korean chicken farms and live bird markets from 2009 to 2014. A total
of 156 H9N2 AIVs was isolated, and we compared the genetic characteristics of theAIV isolates withH5N1 and H5N8 highly
pathogenic influenza viruses (HPAIVs) isolated in Korea. Phylogenetic analysis classified the H9N2 AIVs into three categories
of genotypes and showed that genetic reassortment had occurred among H9N2 AIVs, HPAIVs and AIVs isolated from wild
birds. The first group of H9N2 AIVs were closely related to A/chicken/Korea/01310/2001 H9N2 (01310) which has been used
for an H9N2 vaccine strain in Korea. The other two groups showed there assortment of polymerase genes each other between
H9N2 AVI and HPAIV. The PB1 genes were similar to H5N8 HPAIV isolated in 2014, and the PB2 genes were closely related
to H5N1 HPAIs. The PA genes of the second group were from 01310-like lineage, but those of the third group from HPAIVlike
lineage. Considering that many kinds of the similar genetic reassortants of H9N2 AIVs have been reported in the several
East Asian countries and H9N2 AIVs are thought as one of the potential pandemic candidates, continuous surveillance and
monitorings should be conducted and investigated for the control of further epidemics.
Biography
Jin-Wook Jang is a student in Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi