Our Group organises 3000+ Global Conferenceseries Events every year across USA, Europe & Asia with support from 1000 more scientific Societies and Publishes 700+ Open Access Journals which contains over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Open Access Journals gaining more Readers and Citations
700 Journals and 15,000,000 Readers Each Journal is getting 25,000+ Readers
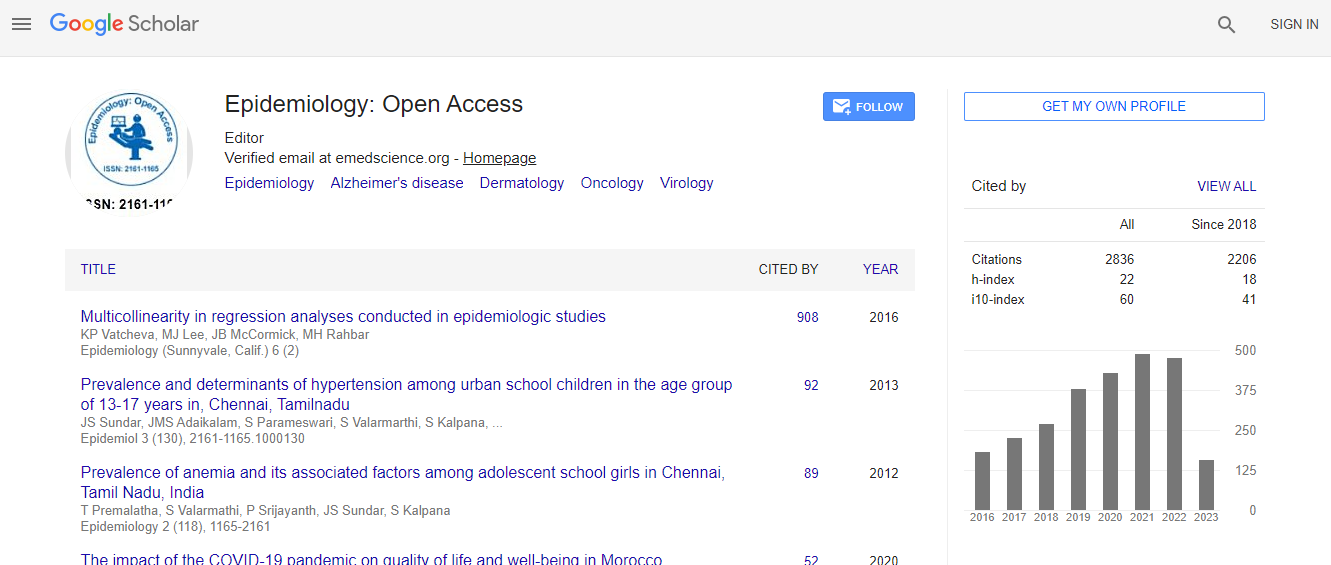
Google Scholar citation report
Citations : 2820
Epidemiology: Open Access received 2820 citations as per Google Scholar report
Epidemiology: Open Access peer review process verified at publons
Indexed In
- Index Copernicus
- Google Scholar
- Sherpa Romeo
- Genamics JournalSeek
- SafetyLit
- Access to Global Online Research in Agriculture (AGORA)
- Centre for Agriculture and Biosciences International (CABI)
- RefSeek
- Hamdard University
- EBSCO A-Z
- OCLC- WorldCat
- CABI full text
- Cab direct
- Publons
- Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
Useful Links
Recommended Journals
Related Subjects
Share This Page
Oxidative inhibition of erythrocyte sodium pump: A functionally relevant circulating marker of oxidative stress
3rd International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health
Chia-chi Liu
ScientificTracks Abstracts: Epidemiology (Sunnyvale)
Abstract
Oxidative stress plays critical roles in the pathogenesis of diabetes and heart disease. The activity of Na pump has been shown
to be depressed from the membrane of erythrocyte preparations of these patients coupled with alterations in membrane
protein composition. We had previously discovered that the β1 subunit of the Na pump undergoes oxidative modification by
oxidative stress in vitro (β1-GSS) and this mediates Na pump inhibition. This study aims to develop and validate erythrocyte
β1-GSS as an oxidative stress biomarker in the premier emerging tool for prognosis of pathophysiological oxidative stress in
patients with or at risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and diabetes. The marker is quickly and easily tested from blood using
ELISA; and could be packaged and marketed as a simple kit. The eβ1-GSS biomarker is modified in heart attack, heart failure
and diabetes, and exhibits potential to predict disease progression. With further investment, the eβ1-GSS biomarker could be
developed initially as a versatile CVD prognosis tool for universal pre-hospital diagnostics, CVD-severity risk-stratification,
and as a Companion Diagnostic (Dx) for CVD medications. Subsequently it could be adapted for diabetes.
Biography
Chia-chi Liu is a Research Fellow at the University of Sydney. She majored in Cell and Molecular Biology at Taipei Medical University, Taiwan. She obtained her
second Master degree in Biotechnology at University of New South Wales; and received a PhD in Chemistry and Bio-molecular Science from Macquarie University
in 2007. Her core focus is investigating the relationship between oxidative stress and the sodium pump function. Her research interests include the development of
new diagnostic methods for oxidative damage of the pump; the discovery of new drugs for heart disease; and the design of novel therapeutic proteins for cancer
treatment. She has been awarded an Australian National Heart Foundation Post-Doctoral Fellowship and Sydney University Research Support Fellowship; and is
the inventor for an innovative Australian patent in diagnostic technology.

 Spanish
Spanish  Chinese
Chinese  Russian
Russian  German
German  French
French  Japanese
Japanese  Portuguese
Portuguese  Hindi
Hindi