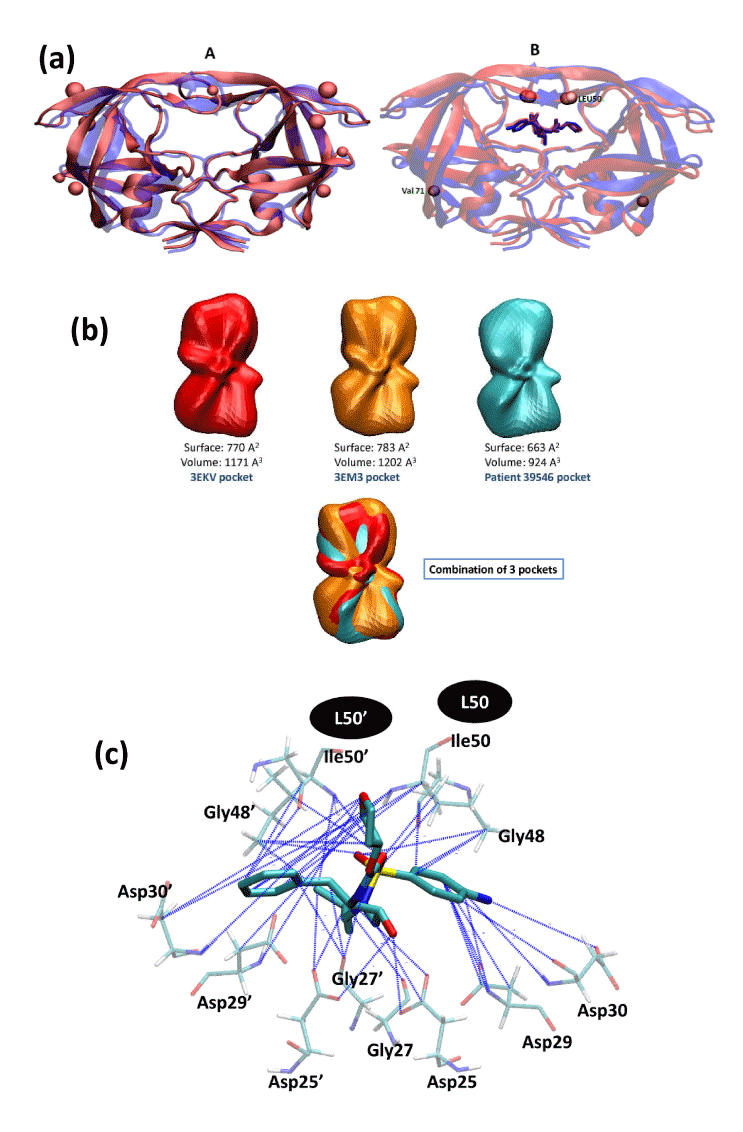
 |
| Figure 3: Several comparisons of mutated HIV protease with the WT protease. |
| (a): The effect of mutations on 3D structures of the HIV-1 protease. The location of each mutation is shown as a ball. |
| Panel A: superposition of the HIV-1 protease 3D structure of patient 39546 (with L15V, E35D, R41K, I50L, V82L mutations) displayed in red (sequencing at time T=0 in HIV-PDI) with the crystal structure of the WT HIV-1 protease shown in purple (PDB entry: 3EKV). Panel B: superposition of the I50L/A71V drug-resistant HIV-1 protease mutant (in red; PDB entry: 3EM3) with the crystal structure of the WT HIV-1 protease (in blue; PDB entry: 3EKV). The two proteases are complexed with APV (displayed as sticks). |
| (b): Spherical harmonic based representations of ligand binding cavities. |
| The cavities of WT HIV-1 protease (PDB code 3EKV), I50L/A71V Drug-Resistant HIV-1 Protease Mutant (PDB code 3EM3), and the HIV-1 protease model structure of patient 39546 are displayed in red, orange, and light blue, respectively. |
| (c): Visualization of the APV interaction pattern. |
| The main protease residues (Asp25, Gly27, Asp29, Asp30, Gly48, Ile50) [24, 25] necessary for drug binding are displayed as sticks. Blue lines highlight interactions lost compared to the WT protease (PDB entry 3EKV) when APV is docked to the I50L mutated protease of patient 39546. |