| Simulation Model | κ | Estimate | Bias | MCSE | Mean of SEs | MSE | CP (%) |
| Increase+Stable | 1 | 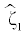 |
-0.122 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 0.015 | 94.4 |
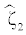 |
-0.010 | 0.022 | 0.021 | 0.001 | 94.5 | ||
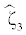 |
-0.014 | 0.021 | 0.021 | 0.001 | 94.8 | ||
| Increase+Decrease | 1 | 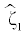 |
-0.071 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 94.9 |
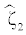 |
-0.088 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.008 | 94.6 | ||
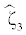 |
-0.068 | 0.009 | 0.009 | 0.005 | 95.4 | ||
| Decrease+Stable | 1 | 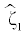 |
0.049 | 0.079 | 0.079 | 0.009 | 94.8 |
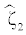 |
-0.026 | 0.064 | 0.063 | 0.005 | 94.4 | ||
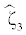 |
-0.009 | 0.065 | 0.064 | 0.004 | 94.5 |
Abbreviations: NB=Negative binomial; PWNB=Piecewise negative binomial; MCSE=Monte Carlo standard error; SE=Stand error; MSE=Means square error; CP =95% CI coverage probability; κ=Overdispersion parameter