 |
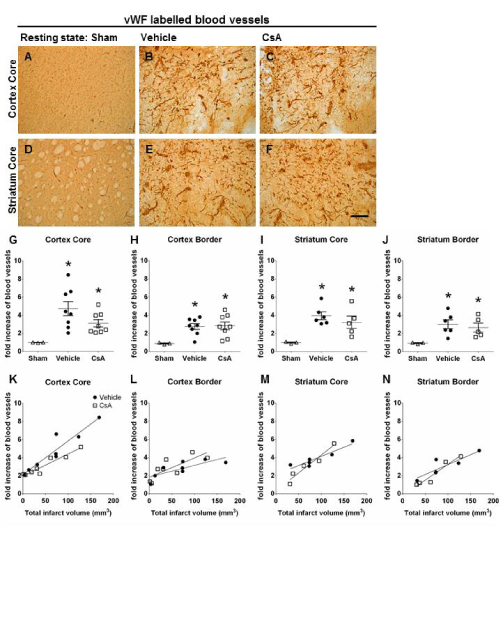
| Figure 5: Effect of CsA on angiogenesis and correlation with infarct volume 7 days following ET-1 induced stroke. Immunohistochemical photomicrographs of vWF staining in consistent sample areas from the ipsilateral hemisphere of shamoperated controls demonstrating normal vascularisation (A, D) and the ipsilateral core damaged regions of the cortex (B, C) and striatum (E,F) demonstrating blood vessel hyperdensity consequent to angiogenesis from both treatment groups at 7 days post-stroke. No difference was observed between vehicle and CsA treated animals in the number of blood vessels detected in all regions used for analysis (G-J, ANOVA). Data are presented as mean ± SEM, *P<0.05 compared to sham-operated animals. A positive correlation was observed between infarct volume and core cortical (vehicle: r=0.94 P<0.001, n=8, CsA: r=0.95, P<0.0005, n=8; K), bordering cortical (vehicle: r=0.79, P<0.05, CsA: r=0.78, P<0.05; L), core striatal (vehicle: r=0.93, P<0.01, CsA: r=0.97, P<0.01; M) and bordering striatal areas (vehicle: r=0.88, P<0.05, CsA: r=0.96, P<0.01; N) for both treatment groups (Pearson product moment correlation coefficients). Scale bars A-F = 200 μm. vWF: von willebrand factor; CsA: Cyclosporine A. |