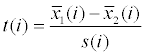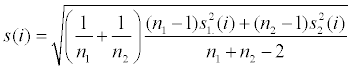| Methods | Formula with relevant details | FDR computation | Note |
| T-test |
|
Benjamini-Hochberg method | Assumes normal distribution |
| SAM | 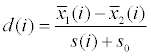 where  and s(i) are the same as in T-test. s0 >0 is a constant added to avoid the dependency of d(i) on the protein abundance level. and s(i) are the same as in T-test. s0 >0 is a constant added to avoid the dependency of d(i) on the protein abundance level. |
permutation-based approach | |
| LIMMA | 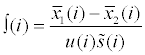 where  is the same as in T-test, is the same as in T-test,  is the posterior residual variance, a weighted average of prior and residual variance; u(i) is the unscaled standard deviation. is the posterior residual variance, a weighted average of prior and residual variance; u(i) is the unscaled standard deviation. |
Benjamini-Hochberg method | A linear model to determine differential expression |
| Wilcoxon rank sum test | 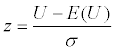 where 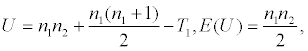  and ni is sample size for group i, T1 is sum of ranks for group 1. and ni is sample size for group i, T1 is sum of ranks for group 1. |
Benjamini-Hochberg method | Non parametric, normal distribution approximation |
| Rank Product |  , , where rlup(i) (or rldown(i), respectively) are the ranks of protein i in the ordered protein lists of length kl sorted in decreasing or increasing order for replicate l; n is the total number of replicates. |
permutation-based approach | Non parametric |
| ROTS (maximize the reproducibility of detections in a family of modified t-statistics) | 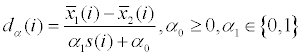 where  and s(i) are the same as in T-test. The parameters α0 and α1 are determined so that they maximize the reproducibility Z- score and s(i) are the same as in T-test. The parameters α0 and α1 are determined so that they maximize the reproducibility Z- scoreZk,a = (Rk,a- R0k,a) / sk,a , where k is the top list sizes; α = (α0, α1);Rk,α and R0k,α are the observed and random reproducibility; sk,α is the standard deviation of the bootstrap distribution. Reproducibility is the overlap of the top-ranked proteins across bootstrap re-samples. |
permutation-based approach | Special cases: the T-test (α0 = 0, α1 = 1), the signal log-ratio (α0 = 1, α1 = 0), the SAM statistic (α1 = 1, α0 is a percentile of the standard deviation). |