 |
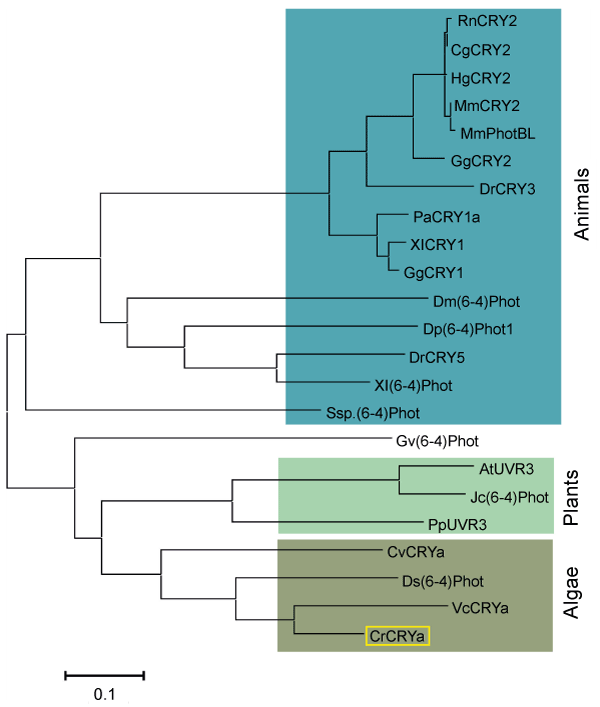
| Figure 1: Phylogenetic tree of the cryptochromes from algae, plants and animals. The tree was constructed by the maximum likelihood method based on amino acid sequences of cryptochrome domain using the MEGA software version 5 [20]. The scale bar indicates the number of substitutions per site. CrCRYa (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), VcCRYa (Volvox carteri), Ds(6-4)Phot (Dunaliella salina), CvCRYa (Chlorella variabilis), PpUVR3 (Physcomitrella patens), Jc(6-4)Phot (Jatropha curcas), AtUVR3 (Arabidopsis thaliana), Gv(6-4)Phot (Gloeobacter violaceus PCC 7421), Ssp.(6-4)Phot (Salpingoeca sp. ATCC 50818), Xl(6-4)Phot (Xenopus laevis), DrCRY5 (Danio rerio), Dp(6-4)Phot1 (Daphnia pulex), Dm(6-4)Phot (Drosophila melanogaster), GgCRY1 (Gallus gallus), XlCRY1 (Xenopus laevis), PaCRY1a (Phreatichthys andruzzii), DrCRY3 (Danio rerio), GgCRY2 (Gallus gallus), MmPhotBL (Mus musculus), MmCRY2 (Mus musculus), HgCRY2 (Heterocephalus glaber), CgCRY2 (Cricetulus griseus) and RnCRY2 (Rattus norvegicus). |