 |
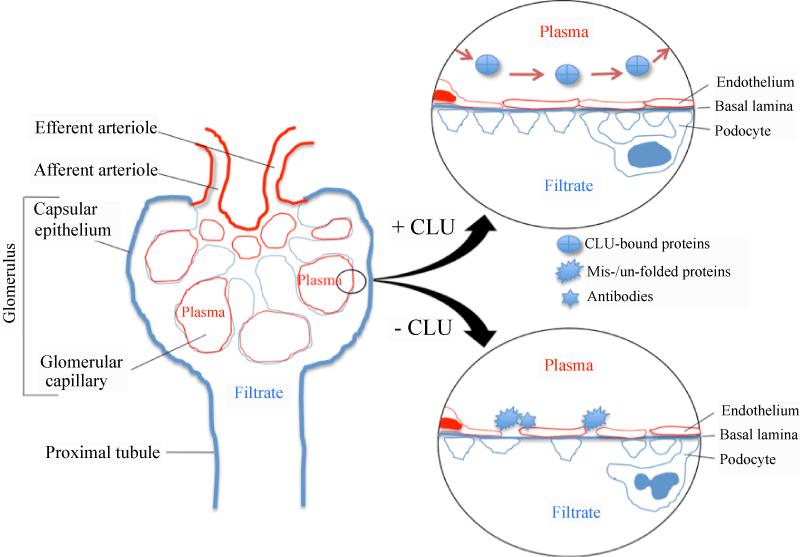
| Figure 3: A simple scheme of hypothesis for the cytoprotection of sCLU in the kidney. Under normal condition or when physiological stress is minimal (+ CLU), sCLU in the plasma acts as a non-specific extracellular chaperone for all kind of mutant, misfolded and unfolded proteins, and prevents autoimmune response to and renal deposition of these ‘nephrotoxic’ proteins. Serum sCLU may also facilitate the protein clearance and intracellular sCLU maintains tissue homeostasis in the kidney. When the physiological stress is increased or under certain pathological condition (- CLU), misfolded and/or unfolded proteins are up-regulated both in the plasma and inside the cell. As a result, there is not enough sCLU to neutralize the accumulation of these proteins – leading to the immune activation and the deposition of these proteins in glomerular capillaries, and renal cell death via ER stress. |