Hemant J Vira and Vivek G Bhat
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0444.1000482
Infectious diseases are a major cause of morbidity and mortality throughout the world. Cancer patients are immunocompromised due to the disease itself and also due to multiple factors such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, impairment of normal leukocyte function, and use of corticosteroids. This leads to development of resistant pathogens in them of which the New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) is mostly resistant to the drug of last resort the class of carbapenems. The increase in extended spectrum carbapenem resistance class of antibiotic has led to a worldwide need for a development of a more efficient and novel class of drug active against NDM-1 producing gram-negative bacteria. The epidemiological study of NDM-1 gene has revealed a startling fact on the widespread prevalence of extended spectrum carbapenem resistant gram-negative bacteria in cancer patients both nationally and internationally. Pharmacovigilance and formulations of different class of antibiotics are needed to tackle the problem of this widespread resistance. The various drug delivery methods and drug designing platforms are needed for the development of a novel class of drug needed to efficiently eradicate these multidrug resistant gram-negative pathogens. In the present review, we have described the epidemiological prevalence of NDM-1 and its variants producing gram negative bacilli in cancer patients both nationally and internationally, the problem of ineffectiveness of carbapenem class of antibiotics against such pathogens, and also the future line of developments needed in the field of pharmacovigilance and pharmacotherapeutics to develop a highly efficient, target specific, and cost-effective class of antibiotics.
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0444.1000e111
Simha Pulla Reddy, Gudi Yamini, Donthamsetty V Sowmya, Venkatapuram Padmavathi and Adivireddy Padmaja
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0444.1000483
A new class of 3,5-disubstituted pyrazoles and isoxazoles were prepared from the Michael acceptors 1-furanyl / thiophenyl / pyridinyl-3-indole-prop-2-en-1-ones under ultrasonication and evaluated for antimicrobial activity. Amongst all the tested compounds fluoro substituted thiophene linked compounds 12b and 18b displayed promising antibacterial activity particularly against Bacillus subtilis and antifungal activity against Aspergillus niger. Furthermore, compounds with more number of electron withdrawing groups showed higher antimicrobial activity. This result indicates that compounds 12b and 18b can be used as lead compounds in the future studies.
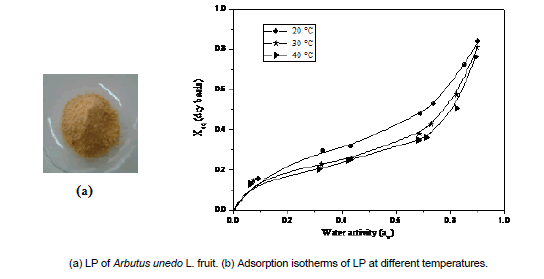
Tounsia Abbas-Aksil, Moussa Abbas, Mohamed Trari and Salem Benamara
The present work aims to investigate the moisture adsorption characteristics of Lyophilized Algerian Arbutus unedo L. fruit powder (LP). First, the LP was evaluated for some of its physicochemical parameters, including X-ray diffraction (XRD) properties, crude fiber, titrable acidity, etc. Second, the experimental sorption curves, determined at 20, 30 and 40°C with the standard static-gravimetric method, were fitted to six isotherm models (Kühn, Caurie, Smith, Halsey, Oswin and GAB). Based on XRD pattern, LP seemed to contain essentially amorphous sugar. Results showed also that the moisture adsorption isotherms of LP are of S-shaped profile (Type II), generally obtained for biomaterials. Among all tested models, those of Halsey and GAB (T=20 and 30°C) gave the best fits at 20 and 30°C, with the mean relative percentage deviation modulus (E%) less than 1%, χ2 ≤ 2.68 10-1 and a root mean square error (RMSE) ≤ 0.2808). The K parameter of GAB model was found to increase with increasing temperature, whereas the monolayer moisture content (X0) decreased with increasing temperature. Such data are represent a useful tool for choose appropriate storage conditions of LP.
Graphical Abstract
Wei Wu, Xiaohong Dai, Wei Zou, Xueping Yu, Wei Teng, Xiaowei Sun, Weiwei Yu, Huihui Ma, Qiuxin Chen, Peng Zhang, Tingting Yu and Peng Liu
Background: Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a life-threatening disease that confuses us for centuries. Acupuncture as a kind of Chinese traditional treatment has been empirically established and widely used in clinics in China, especially for stroke victims. Studies proved that GV20 penetrating GB7, a kind of needling manipulation, with which a needle is inserted into GV20 and then to GB7 under the scalp, is especially effective on the treatment of this disease. Wingless-type1 (Wnt1) is a key factor of Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway, which could promote regeneration and remodeling of neural function after ICH by affecting proliferation and differentiation of the neural stem cells (NSCs). The study on the expression of Wnt1 induced by GV20 penetrating GB7 may give out the theoretical principle of the treatment.
Objective: The goal of this work is to observe the effect of GV20 penetrating GB7 needling on the protein/ mRNA expression of Wnt1 in brain tissue of ICH rats.
Methods: In this experiment, we focused on observing the protein/mRNA expression level of Wnt1 by Western blot and real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (RTFQ PCR) in the rats with ICH, which were treated by Dickkopfrelated protein 1 (DKK1), acupuncture or no intervention, comparing with the healthy rats without any treatment at fixed time points.
Results: This study revealed that the expression of Wnt1 had the similar trend in all groups at each time point of corresponding treatment, which began to increase from the third day (3d), reached the peak on the seventh day (7d) then decreased gradually. The acupuncture treatment group showed a higher level of expression.
Conclusion: The results show that GV20 penetrating GB7 has advantage on promoting the protein/mRNA expression of Wnt1, activates the intracellular Wnt pathway, and regulates the transcription of downstream target genes, affecting proliferation and differentiation of the neural stem cells (NSCs), thereby initiates endogenous repair mechanisms of the organism itself. This study provides a powerful scientific basis for acupuncture treatment on ICH.
Li-Fei Bai, Hui-Hong Qian, Da-Wei Jiang, Xiao-Ming Wang and Ren-Lei Wang
In this study, a series of Dinitrodiphenyl Ether derivatives (1b-5b) were synthesized and their biological activities were also evaluated as potential tubulin inhibitors. Among them, compound 3b (IC50=1.26 ± 0.84 μM) exhibited the most potent anti-proliferative activity of MCF-7 cancer cell line in vitro, which was comparable to that of colchicine (IC50=0.93 ± 0.46 μM) as reference. And it also showed the most potent growth inhibitory activity against tubulin (IC50=5.10 ± 0.81 μM), which was also compared with colchicine (IC50=3.42 ± 0.63 μM). Molecular docking simulation results demonstrated that 3b could bind to the colchicine binding site of tubulin and effectively inhibit tubulin polymerization. Moreover, the subsequent cell cycle arrest and apoptosis assay further confirmed that 3b could cause MCF-7 cell cycle arrest in the middle and later stages of mitosis and thus leading to cell apoptosis. To sum up, we recommend 3b as the best candidate of potential anti-cancer agent among these new compounds. Based on the preliminary results, compound 3b with potent inhibitory activity in tumor growth may be a potential anti-cancer agent.
L Arabuli, R Jezek, T Macek, P Lovecka, E Nikoleishvili, N Sulashvili and I Maisuradze
DOI: 10.4172/2161-0444.1000487
The new small peptide functionalized cyclen and DOPA derivatives were synthesized: cyclen-HisHis, cyclen- AspHis, cyclen-GluHis, DOPA-HisHis were prepared. The solid-phase synthesis strategy was used for preparation of new compounds. Synthesized cyclen- and DOPA-oligopeptide hybrid conjugations were purified by HPLC and analyzed using MALDI-TOF MS spectrometer. The toxic effect was determined against mammalian cells human embryonic kidney cell line HEK293T ATCC®CLR-11268TM for each new compound. The inhibition effect of all tested cyclen– dipeptides on kidney cells was approximately about 30% after 24 hours. The minimal rate of toxicity against human liver cells showed all tested dipeptides with DOPA, their inhibition effect was maximal 10%. The acute inhibition effect of sample DOPA-GluHis-DOPA was 14% imme¬diately after adding. The antioxidant and anticancer activity studies will be next part of the ongoing project.
Medicinal Chemistry received 6627 citations as per Google Scholar report