 |
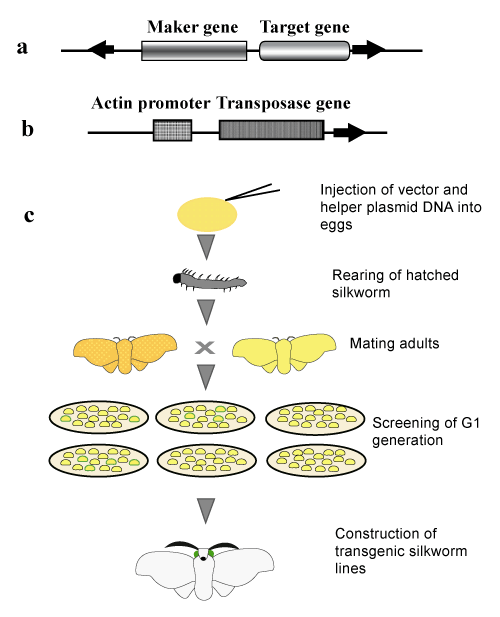
| Figure 2: Structures of the vector (a) and helper plasmid (b). (c) Process for generating transgenic silkworms by injecting vector and helper plasmids into preblastoderm eggs. The vector plasmid possesses a marker gene for the screening of transgenic silkworms and a target gene between the two ITRs (filled arrows). The helper plasmid carries the piggyBac transposase gene under the control of the silkworm cytoplasmic actin gene promoter. Transgene integration occurs during the embryonic stage in G0 silkworms. The hatched silkworms are reared on an artificial diet or fresh mulberry leaves and the adults are mated with each other to obtain G1 silkworm eggs. When the 3xP3EGFP gene is used as a marker gene (see Figure 3), the transgenic silkworms can be screened at the embryonic stage. |