 |
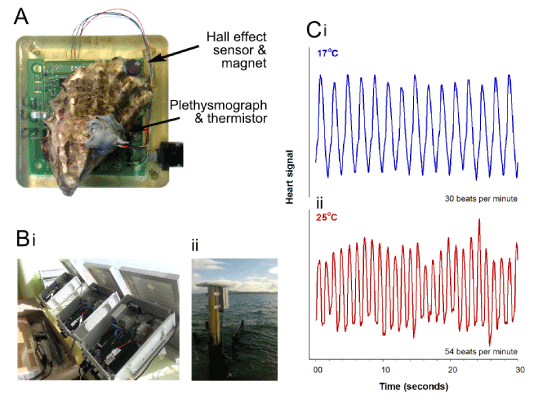
| Figure 1: (A) Anoyster attached to UTAS/CSIRO oystag biosensor. The LED plethysmograph and thermistor are inserted through a small (<4 mm diameter) hole in the shell. A magnet attached to the top shell and the hall effect sensor on the printed circuit board (PCB) beneath are used to determine valve activity (i.e. shell gape). Additional sensors on the PCB are pressure (to inform depth), lux (light intensity) and ambient temperature. (Bi) The AgISP telemetry node and environmental sensors during preparation for installation and in the field. (Bii) The node transmits data from the oystag and environmental sensors to a data cloud via 4G technology. (C) A representative oyster heart rate trace from the data cloud showing an increase in heart rate from 30 BP Mat 17°C (i) to 54 BPM at 25°C (ii). |