 |
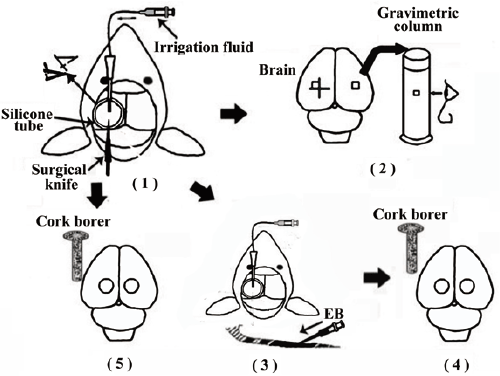
| Figure 5: Schematic diagram of the experimental protocol. An burr hole was made in the left side of the skull through the silicone tube. Via the burr hole, irrigation with each solution was started, and the dura mater, arachnoid membrane, and cerebral cortex were incised crosswise in the area of the opening with a microsurgical knife. The dura mater and arachnoid mater were removed from the injured area (1). Part 1: Four hours after injury, brain tissue samples were obtained from the area facing the intersection of the wound (injured site) and from the area asymmetrically opposite to the injured site in the uninjured contralateral hemisphere (uninjured site). Samples were then placed in a gravimetric column (2). Part 2: Two percent of EB in saline was given intravenously 3 hours after injury (3). Four hours after injury, irrigation was stopped. To remove the intravascularly localized dye, we perfused with normal saline. Using 4-mm-diameter cork borer, brain tissue samples were obtained from the area of the wounds (injured site) and from the area symmetrically opposite to the injured site in the uninjured contralateral hemisphere (uninjured site). Extraction and determination of EB dye were then performed (4). Part 3: Using a 4-mm-diameter cork borer, brain tissue samples were obtained from the area of the wounds (injured site) and from the area symmetrically opposite to the injured site in the uninjured contralateral hemisphere (uninjured site). Then, TTC incubation and measurement of tissue formazan were performed (5). [Modified with permission from reference [7]]. |