 |
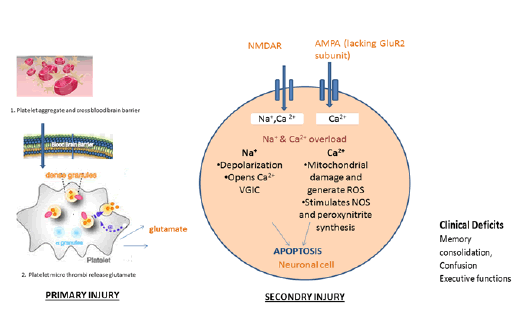
| Figure 1: Primary injury is caused due to formation of microthrombi and crossing of blood-brain barrier. Microthrombi accumulate in neuronal parenchyma and release glutamate, which stimulates glutamate ionic receptors i.e. NMDAR and AMPAR. Secondary injury is caused due to over-stimulated glutamate ionic receptors, which disrupt ionic balance leading to two consequences: either apoptosis by triggering mitochondrial damage and forming reactive oxygen species or causing clinical deficits. (NMDAR, Nmethyl- D-aspartate receptor; AMPAR, α amino-3-hydroxy-5- methyl-4-isoxazoepropionic acid receptor; VGIC, Voltage-gated ion channel; NOS, Nitric oxide synthase). |