 |
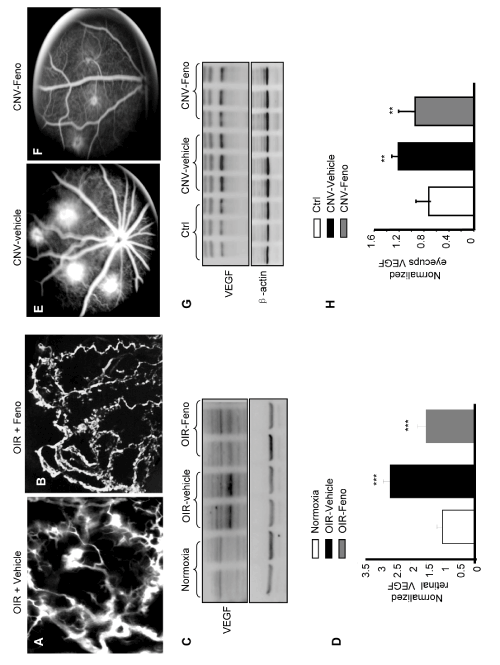
| Figure 4: Topical fenofibrate application reduces retinal vascular leakage and prevents NV in OIR and laser-induced CNV rats. (AD) Rats were exposed to 75% oxygen from P7 to P12. Following a return to normoxic conditions, rats were topically administered fenofibrate (15 μl/eye, 4 times/day for 5 days), and an identical volume of the vehicle served as the control. (A,B) At P17, the retinal vasculature and leakage was visualized using fluorescein angiography. (C,D) representative Western blot analysis of retinal VEGF levels at P16 in equivalent amounts (50 μg) of retinal proteins using an antibody against VEGF, and β-actin served as a loading control. Each lane represents an individual rat. Compared to the vehicle, fenofibrate eyedrops significantly reduced retinal VEGF levels induced by hypoxia (mean ± SD, n=4; *** P<0.001 OIR-vehicle vs. normoxia; $$$P <0.001 OIR-vehicle vs. OIRfenofibrate). (E-H) Adult rats underwent laser coagulation followed by the topical administration of fenofibrate (15 μl/eye, 4 times/day for 21 days), and an identical volume of vehicle served as the control. (E,F) A representative fundus angiography was taken at day 21. (G,H) Equivalent amounts (50 μg) of total protein from the eyecups were probed using an antibody against VEGF, and β-actin served as the loading control. Each lane represents an individual rat. Compared to the vehicle, fenofibrate eyedrops significantly reduced retinal VEGF levels induced by hypoxia (mean ± SD, n =3, **P <0.01 CNV-vehicle vs. control; $$$P < 0.001 CNV-vehicle vs. CNV-fenofibrate). |