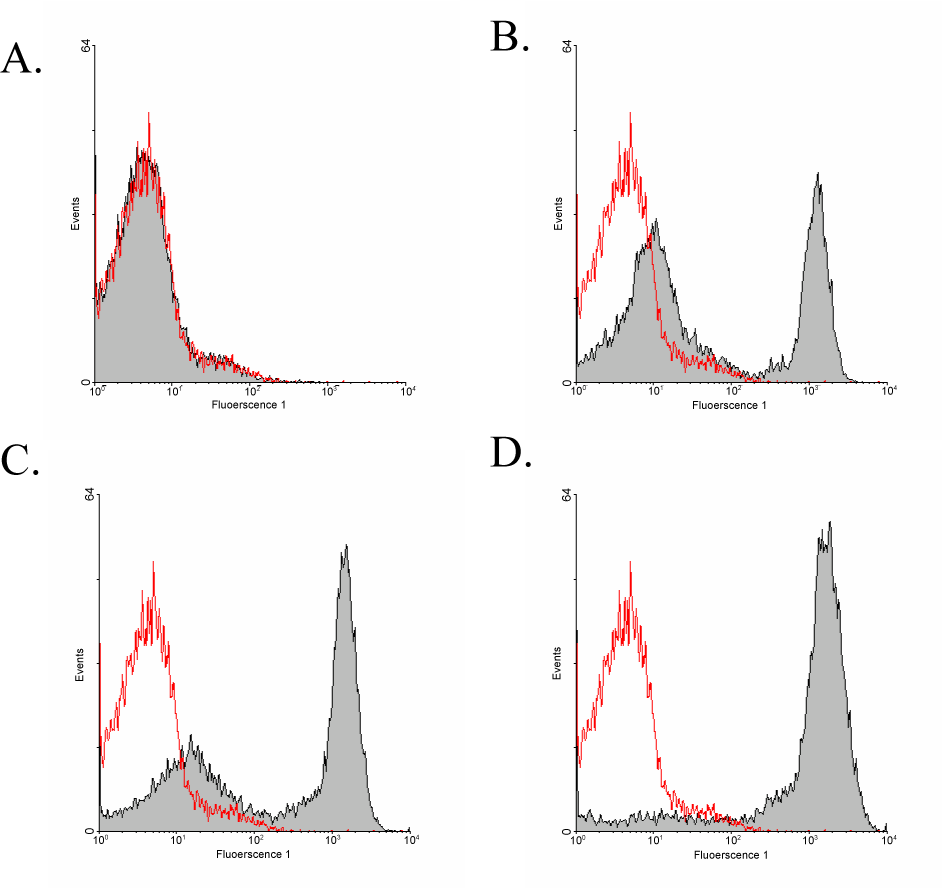
 |
| Figure 2: Effect of increasing concentrations of ciprofloxacin to the membrane potential of S. pneumoniae. Toxicity of ciprofloxacin resulted in depolarisation of membrane potential followed by increased binding of DiBAC4(3) indicated by increased fluorescence intensity (grey filled histogram). Red line: Bacteria not treated with ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin concentrations were A) 0.015 μg/ml B) 0.125 μg/ml C) 1μg/ml D) 4 μg/ml. |