 |
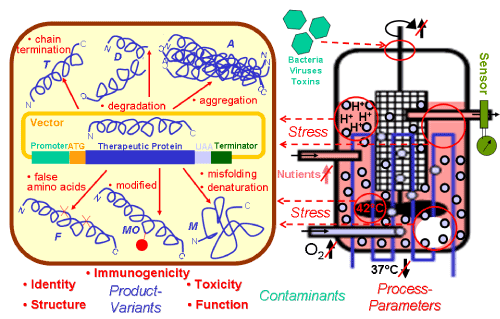
| Figure 1: Errors and heterogeneity in the biotechnological production of protein drugs. Ectopic expression of protein drugs in recombinant host cells, such as bacterial, yeast and mammalian cells may lead to multiple product variants (T, D, A, F, MO, M) due to the operation of multiple physiological and stress response pathways under normal and sub-optimal growth conditions, respectively. Critical parameters for the quality of the resulting product variants may be differentially affected and become further impaired during fermentation in the large scale. The accompanying sub-optimal process parameters will lead to cellular stress due to local nutrient and oxygen depletion or pH and temperature increase. These deviations from the optimal process will not be recognized by sensors operating outside of the bioreactor. Furthermore, bioreactors are susceptible for infiltration by contaminants. A, aggregated protein; D, degraded protein; F, protein with false amino acids incorporated; M, misfolded denatured protein; MO, posttranslationally modified protein; T, prematurely terminated protein. |