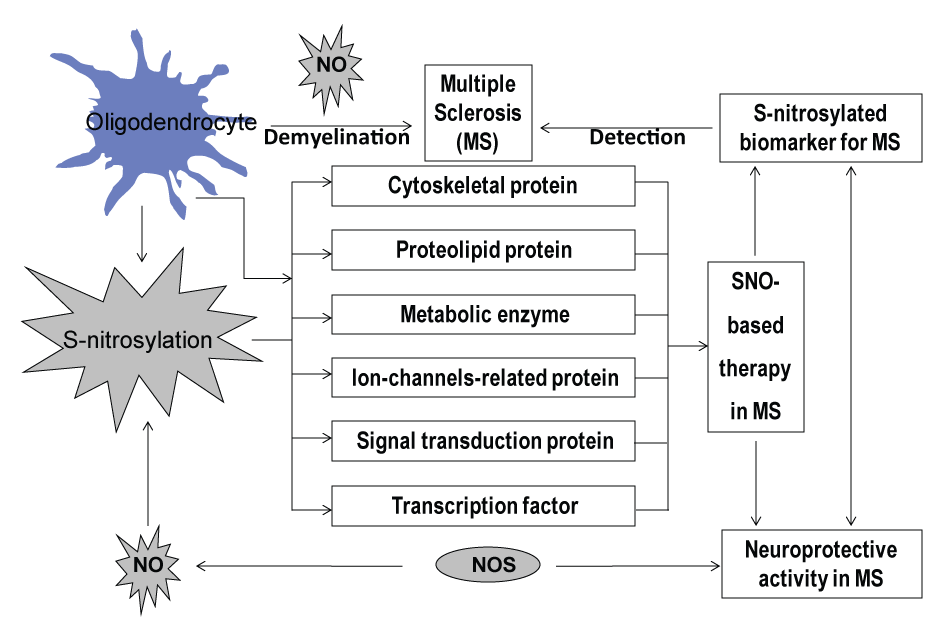
Protein SNOs accumulate in the brain of MS patients and SNO levels are also increased in EAE, indicating that the occurrence of protein S-nitrosylation correlates with the inflammatory demyelinating disorders in MS patients. Oligodendrocyte injury and inflammatory demyelination are key pathological abnormalities of MS and its animal model EAE. The S-nitrosylation target proteins include cytoskeleton proteins, proteolipid protein, metabolic proteins, ion channel proteins, signaling proteins, and transcription factors. Then S-nitrosylation of proteins could be a potential therapeutic strategy in MS. The S-nitrosylated protein biomarkers are helpful for the early diagnosis, prognosis, evaluation of the development of the disability caused by the disease and the response to therapy. Activation of iNOS and NO generation was identified as a marker and therapeutic target in neuroinflammatory conditions in MS. Protein SNOs accumulate in the brain of MS patients and SNO levels are also increased in EAE, indicating that the occurrence of protein S-nitrosylation correlates with the inflammatory demyelinating disorders in MS patients. Oligodendrocyte injury and inflammatory demyelination are key pathological abnormalities of MS and its animal model EAE. The S-nitrosylation target proteins include cytoskeleton proteins, proteolipid protein, metabolic proteins, ion channel proteins, signaling proteins, and transcription factors. Then S-nitrosylation of proteins could be a potential therapeutic strategy in MS. The S-nitrosylated protein biomarkers are helpful for the early diagnosis, prognosis, evaluation of the development of the disability caused by the disease and the response to therapy. Activation of iNOS and NO generation was identified as a marker and therapeutic target in neuroinflammatory conditions in MS.