 |
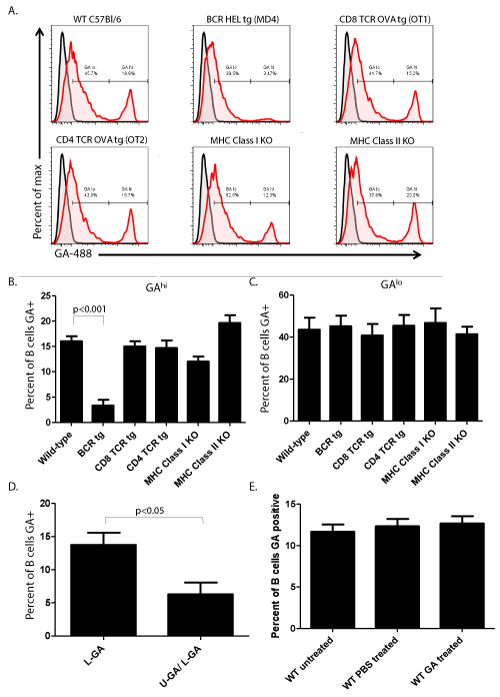
| Figure 1: GA binds to the B cell receptor, and in vivo administration of GA in a non-inflammatory environment does not expand GA specific B lymphocytes. Single cell suspensions of splenocytes from the indicated mice were incubated with 488 conjugated GA and stained with antibodies specific for T cells, B cells, macrophages, and NK cells. The percent of GA+ immune cell populations was determined by flow cytometric acquisition and analysis. Shown is the data generated for B lymphocytes. (A) GA non-specifically associates with B cells as shown by the GAlo gated population and specifically binds to the B cell receptor as shown by reduced binding in the GAhi population on BCR-HEL tg B lymphocytes. Black lines represent the staining profile of 488 alone, while the red lines represent the staining profile with 488-GA. Data is representative of three individual experiments. (B) The reduction in the GAhi population on B lymphocytes from BCR-HEL tg animals is statistically significant. The reduction in the proportion of GAhi B cells from MHC Class I KO animals and the increased proportion of GAhi B cells from MHC Class II KO animals was not statistically significant. The graph shows the average proportion of GAhi B cells ± SD from three separate experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis with Dunnett post-test. (C) The proportion of GAlo B lymphocytes is not statistically different in all mouse strains tested. The graph shows the average proportion GAlo B cells ± SD from three separate experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis with Dunnett post-test. (D) Splenic B cells from wild-type mice were either incubated with labeled GA (L-GA), or unlabeled GA (U-GA) followed by labeled GA. Shown is the percent of B cells GAhi. (E) In vivo administration of GA does not expand GA+ B lymphocytes in wild-type mice. The graph shows the average proportion of GAhi B lymphocytes ± SD from three mice per group. Data is representative of three experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis with Dunnett post-test. |