 |
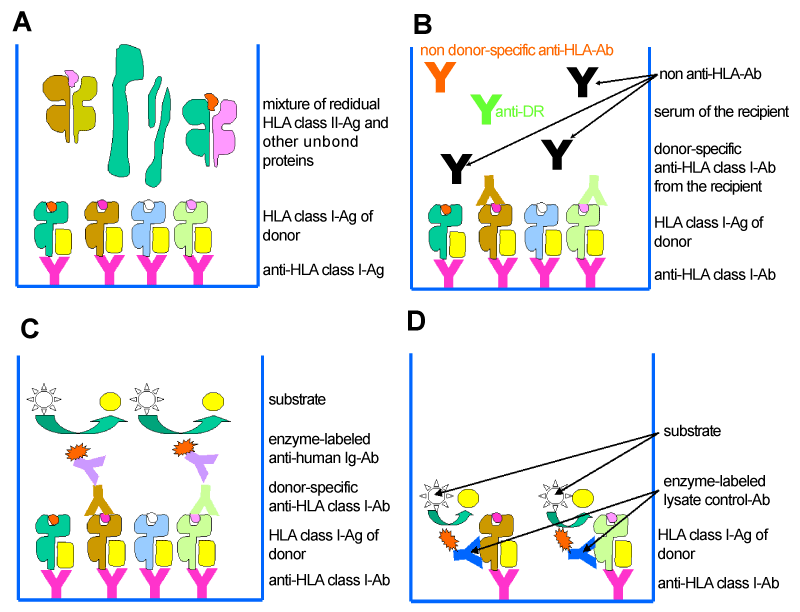
| Figure 2: Flow diagram of the crossmatch-ELISA for the detection of donor-specific anti-HLA class I antibodies. (A) Binding of the donor’s solubilized HLA class I molecules by monoclonal capture antibodies recognizing a monomorphic epitope on HLA class I molecules. (B) Binding of the donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies out of the recipient’s serum to the HLA molecules of the donor. (C) Binding of enzymeconjugated secondary anti-human IgG (anti-human IgG/M/A) antibodies to the bound recipient’s donor-specific anti-HLA class I antibodies and subsequent colour reaction. (D) Lysate control using an enzyme-conjugated monoclonal antibody directed against a second monomorphic epitope for detection in order to confirm the immobilization of a sufficient amount of HLA molecules by the capture antibody to generate a signal. The ELISA-variant for the detection of donor-specific anti-HLA class II antibodies is correspondingly designed. |