 |
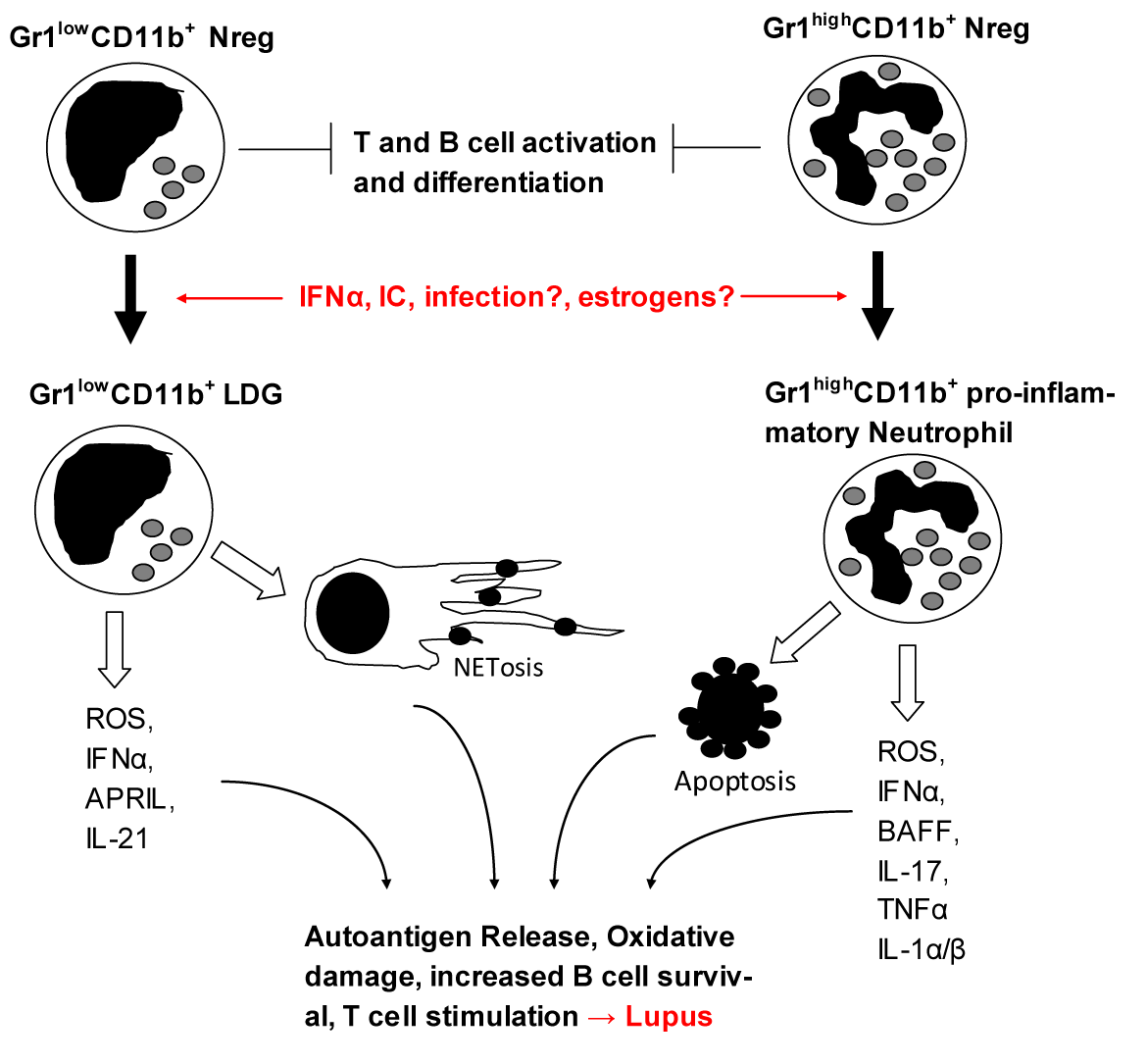
| Figure 1: Neutrophils in Lupus. Model suggesting that a subset of neutrophils (Nregs) possess regulatory abilities involved in the control of humoral immunity. Under non-inflammatory conditions, such Nregs are located to the secondary lymphoid organs where they regulate T and B cell responses to foreign antigen. During chronic inflammation (Lupus), neutrophils display pro-inflammatory abilities including the production of IFNα and secretion of NETs by LDGs, and the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species involved in tissue damage by mature neutrophils. Signals driving the generation of pro-inflammatory neutrophils may include estrogen, IC and cytokines, all of which are associated with the development of lupus in genetically predisposed females. |