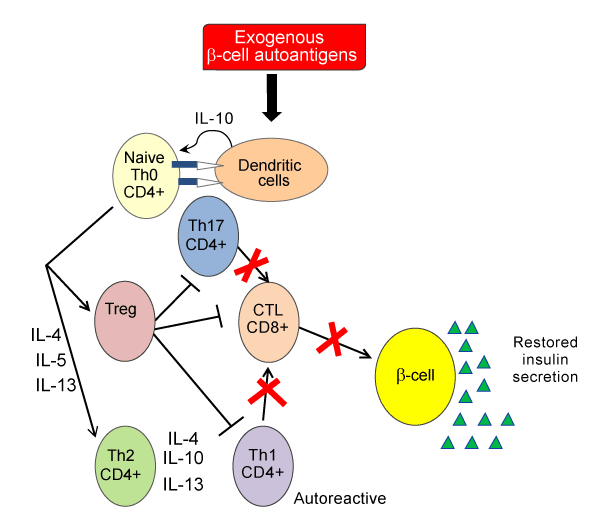
Oral delivery of islets autoantigens induces a protective antigen-specific therapeutic effect. Exogenous β-cell autoantigens stimulate dendritic cells to secrete the anti-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-10 (IL-10), which stimulates naïve Th0 cells to become T helper 2 CD4+ (Th2) cells. Th2 cells suppresses autoreactive Th1 cells and decrease potential insulitis onset. Alternatively, naive Th0 cells may turn into one of several subclasses of regulatory T cells (Treg), which can block not only Th1 cells but also dendritic cells activation, Th2, Th17, and cytotoxic lymphocytes (CTL) leading to prevention or reversion of insulitis and restoring insulin secretion.