 |
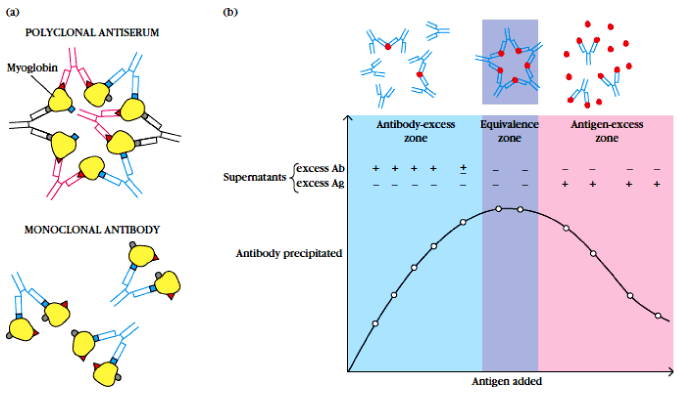
| Figure 1a: (Precipitation reactions description: (a) Polyclonal antibodies can form lattices, or large aggregates, that precipitate out of solution. However, if each antigen molecule contains only a single epitope recognized by a given monoclonal antibody, the antibody can link only two molecules of antigen and no precipitate is formed. (b) A precipitation cur ve for a system of one antigen and its antibodies. This plot of the amount of antibody precipitated versus increasing antigen concentrations (at constant total antibody) reveals three zones: a zone of antibody excess, in which precipitation is inhibited and antibody not bound to antigen can be detected in the supernatant; an equivalence zone of maximal precipitation in which antibody and antigen form large insoluble complexes and neither antibody nor antigen can be detected in the supernatant; and a zone of antigen excess in which precipitation is inhibited and antigen not bound to antibody can be detected in the supernatant). |