 |
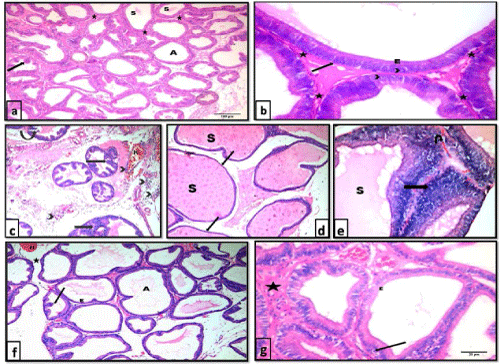
| Figure 1: Photomicrographs of H&E stained sections of the ventral prostate of different groups: a and b) control group showing packed prostatic acini (A) of variable sizes, infolded mucosa (arrow), fibromuscular stroma (*) and homogenous acidophilic secretion (S) in some acini. The prostatic acini are lined with simple columnar epithelium (E) with basal nuclei (arrow head) and intact basement membrane (arrow). a 100X , b 400X. c,d and e testosterone group showing c) widely separated prostatic acini with many papillary folds (arrow), desquamated epithelial cells (curved arrow) and focal areas of epithelial proliferation (notched arrow). Notice the areas of hemorrhage (H) and inflammatory cellular infiltration (arrow head) within the thick fibromuscular stroma. H&E, 100X. d) enormous dilatation of prostatic acini filled with secretion (S) with thinning and flattening of lining epithelium in some areas of the acini (arrow). H&E, 100X. e) an area of epithelial proliferation (arrow) where cells are arranged as multiple unorganized layers. Lumina are distended with secretions (S). Stroma shows areas of hemorrhage (U-turn arrow) H&E, 400X. f) and g) testosterone+ginseng group showing widening of the lumina of the acini (A). Epithelial height is reduced (E) and epithelial folds are diminished (↑). Acini are separated by a reduced amount of fibromuscular stroma (*) that still shows areas of hemorrhage (H). Some epithelial cells show small dark nuclei (arrow). f: 100X; g: 400X. |