 |
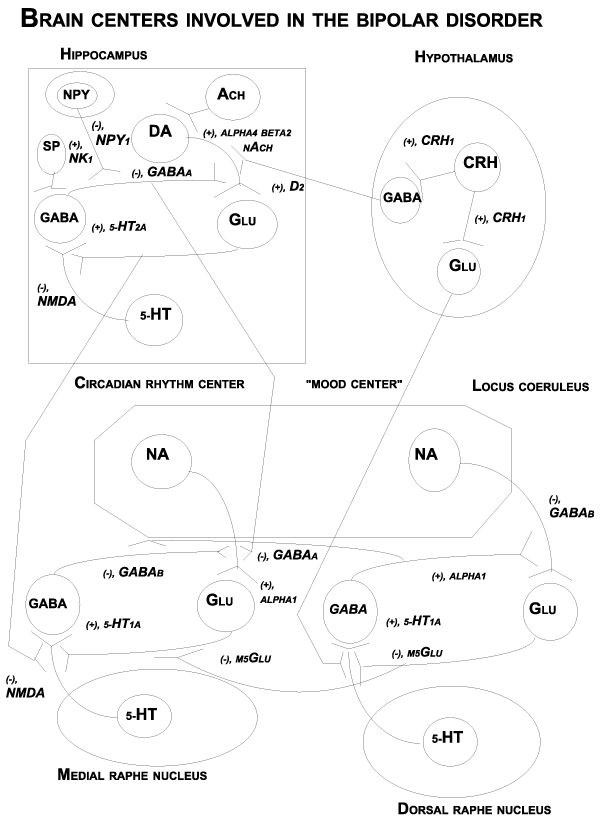
| Figure 1: Neuronal pathways, classical neurotransmitters and neuropeptides involved in bipolar disorder. 5-HT: Serotonin; Ach: Acetylcholine; DA: Dopamine; CRH: Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone; GABA: Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid; Gal: Galanin; Glu: Glutamate; NA: Noradrenaline; NPY: Neuropeptide Y; SP: Substance P. The following subreceptors are indicated: alpha4beta2 nAch: alpha4beta2 nAch, a subreceptor of the nicotinic cholinergic receptor; CRH1: the CRH1 receptor, a subreceptor of the corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor; GABAA: GABAAreceptor, a subreceptor of the GABA receptor; GABAB: GABAB receptor, a subreceptor of the GABA receptor; 5-HT1A: 5-HT1A receptor, a subreceptor of the serotoninergic receptor; 5-HT2A: 5-HT2A receptor, a subreceptor of the serotoninergic receptor; D2: D2 receptor, a subreceptor of the dopaminergic receptor; m5Glu: m5Glu receptor, a subreceptor of the metabotropic glutaminergic receptor; NK1: the NK1 receptor, a subreceptor of the tachykinin receptor; NMDA: NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor, a subreceptor of the ionotropic glutaminergic receptor; NPY1: NPY1 receptor, a subreceptor of the neuropeptide Y receptor. |