 |
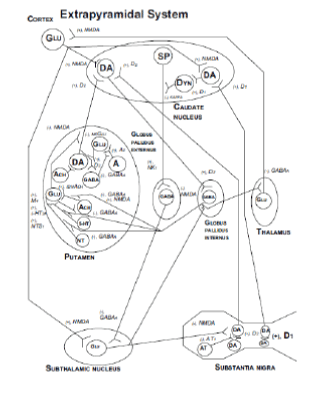
| Figure 1: Neuronal pathways, classical neurotransmitters and neuropeptides involved in Parkinson’s disease in the extrapyramidal system. 5-HT: serotonin; A: adenosine; ACh: acetylcholine; AT: angiontensin; DA: dopamine; Dyn: dynorphin; GABA: gammaaminobutyric acid; Glu: glutamate; NT: neurotensin; SP: substance P. The following subreceptors are indicated: A2A: A2A receptor, a subreceptor of the adenosine receptor; AT1: AT1 receptor: a subreceptor of the angiotensin receptor; ß2nAch: ß2nAch receptor: a subreceptor of the nicotinic cholinergic receptor; GABAA: GABAA receptor, a subreceptor of the GABA receptor; 5-HT2A: 5- HT2A receptor, a subreceptor of the serotoninergic receptor; D1: D1 receptor, a subreceptor of the dopaminergic receptor; D2: D2 receptor, a subreceptor of the dopaminergic receptor; kappa: kappa receptor: a subreceptor of the opioid receptor; M4: M4 receptor: a subreceptor of the muscarinic cholinergic receptor; m5Glu: m5Glu receptor, a subreceptor of the metabotropic glutaminergic receptor; NK1: NK1 receptor: a subreceptor of the substance P receptor; NMDA: NMDA (N-methyl-D-aspartate) receptor, a subreceptor of the ionotropic glutaminergic receptor; NTS1: NTS1 receptor: a subreceptor of the neurotensin receptor. A plus mark indicates a postsynaptic excitatory impulse; a minus mark indicates a presynaptic inhibitory impulse. |