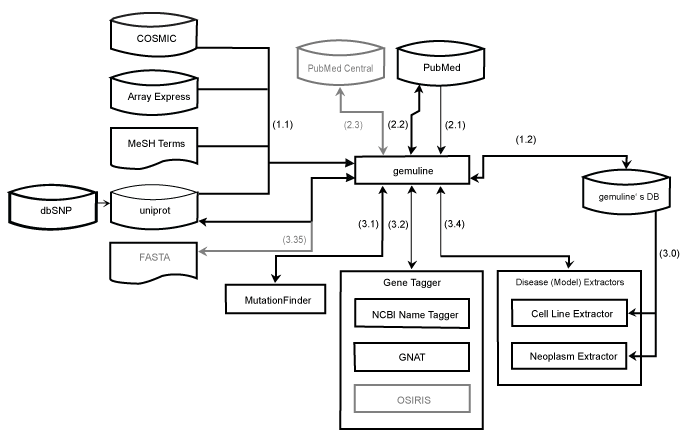
 |
| Figure 2: Workflow of all processes of gemuline in an overview. (1) Updating the data warehouse. Extracting information from data sources (1.1) and writing the processed, combined data into the data warehouse (1.2). (2) Text retrieval. Acquiring PubMed ids from an online query (2.1) and downloading the abstracts (2.2). Optionally, retrieving full text versions (2.3). (3) Information retrieval. First, loading the cell line and neoplasm extractor with aliases from the data warehouse (3.0). Running MutationFinder to get mutation candidates (3.1). Tagging genes with either the NCBI Name Tagger or GNAT (3.2). Originally it was planned to also integrate OSIRIS, but the tool is currently not publically available (see chapter 2.1.10). Matching mutations to genes with Uniprot (3.3). If (3.3) is not possible, gene sequences are checked for a possible mutation at the given position (3.35). Finally, extraction and matching to cell lines or MeSH terms (3.4) takes place. |