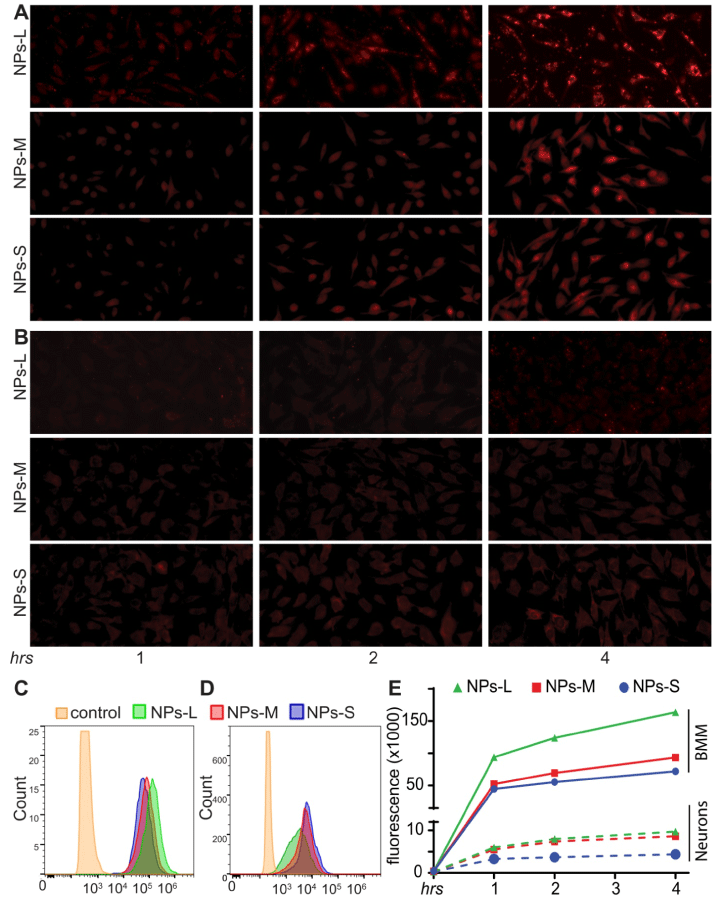
| Small-, medium-, and large-sizes RVG-PTX-nanocomplex Nanocomplex-S, -M and -L were treated to BMM (A) and neurons
(B) for 1, 2 and 4 hrs. Red fluorescence represented intracellular distribution of RVG-PTX-nanocomplex uptake by the cultures.
Representative images of flow cytometry results exhibited the fluorescence signals in BMM (C) and neurons (D) at 4 hrs treated
to three sizes of RVG-PTX-nanocomplexes. The shift of fluorescence distributions indicated the significant levels of all three
sizes of RVG-PTX-nanocomplex uptake by BMM. Quantitation of flow cytometer assay (E) showed that large-size RVG-PTXnanocomplex
enhanced uptake by BMM. An increase uptake profile correlated to the rise of particle size. In contrast, enlarging
size prevented neuronal uptake of RVG-PTX-nanocomplex. A decrease of uptake profile correlated to the rise of particle size. |