 |
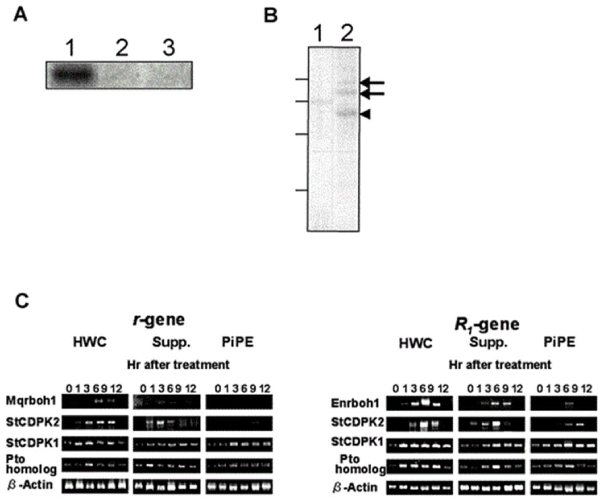
| Figure 5: SdCDPK2 autophosphorylation and RT-PCR gene expression analysis. (a) SdCDPK2 is autophosphorylated by the PiPE and elicitor treatment. Purified His-CDPK2 in phosphorylation buffer (lane 1), phosphorylation buffer containing 2 mM EGTA (lane 2) or phosphorylation buffer containing about 2 μg PiPE (lane 3) was incubated at 30°C for 10 min under the existence of 1 μCi [γ-32P] ATP. Thus treated His-CDPK2 was precipitated, subjected to 12% SDS-PAGE and detected by autoradiography as described in” Materials and Methods”. (b) NADPH oxydase is phosphorylated by His-CDPK2. Microsomal fraction containing NADPH oxydase (lane 1) and purified NADPH oxydase (lane 2) was incubated with purified His-CDPK2 and detected by autoradiography as shown in (a). Arrows indicate His- NADPH oxydase and arrowhead indicates His-CDPK2, respectively. Lines shown on the left side indicate molecular markers, 97, 66, 43 and 29 kDa (up to bottom), respectively. (c) Quantitative RT-PCR of defence signal genes in cv. Eniwa (R1-gene) and Mayqueen (r-gene). After the treatment of elicitor, PiPE, and suppressor of Pi, total RNA was extracted and PCR using the primers (See Methods). All PCR reactions were done at 20 cycles from the result. HWC elicitor and PiPE treatment, and suppressor treatment were observed, and also Pto homologs were observed. |