 |
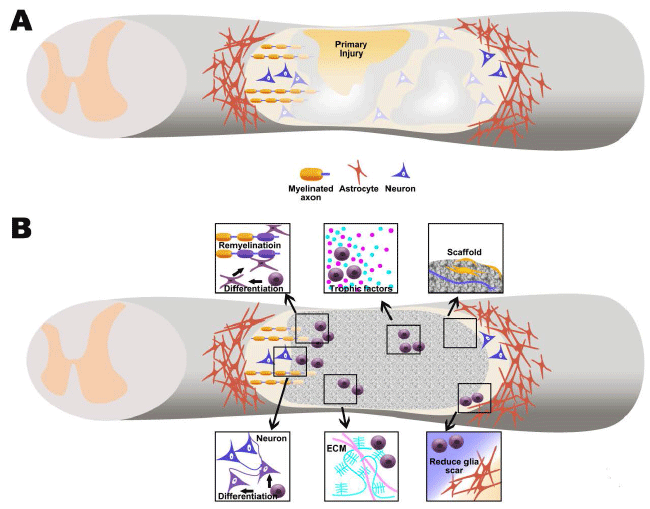
| Figure 1: The pathophysiology of spinal cord injury and the potential mechanism of stem cell based tissue engineering approach in spinal cord injury repair. Primary and secondary injury the damage the spinal cord tissue including neural cell death, nerve fiber breakage, hemorrhagic necrosis and edema and demyelination. With the persistence of inflammation, the glial scars and cavities form, as a barrier for neuroregeneration (A). Possible mechanism of stem cell based tissue engineering approach in spinal cord injury repair, such as the physical support from the biomaterials to fill in the cavities and to work as scaffold for donor and host to migrate and reside. Some biomaterials may contain anti glia scar elements that can promote nerve regeneration. The donor stem cells can differentiate into neurons or glia cells to replenish the lost cells. They can also rectify local hostile microenvironment through secretion of beneficial trophic factors and extracellular matrix (B). |