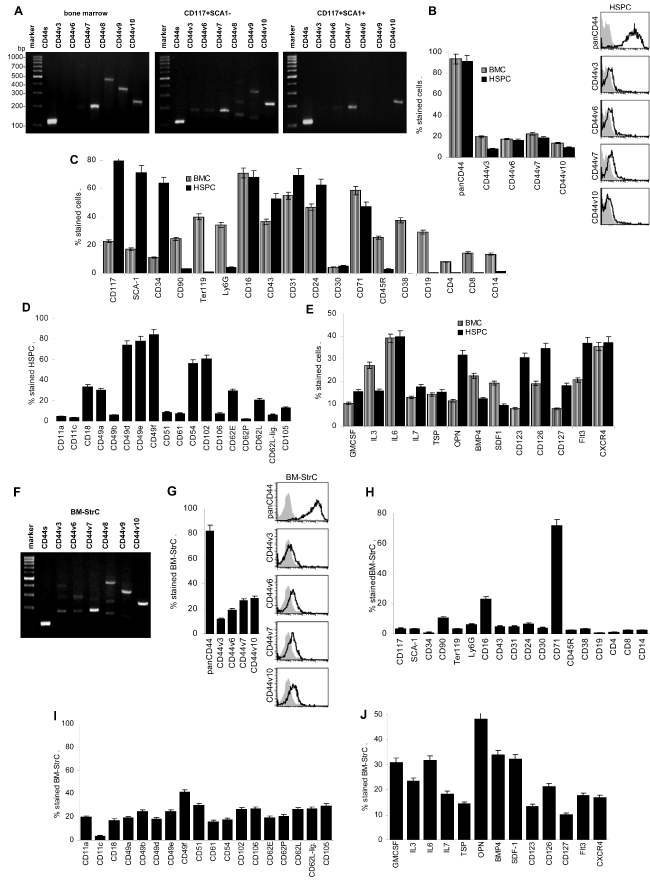
CD44 is highly expressed in unseparated BMC and HSPC. HSPC mostly express single CD44v variant exon products at a low level. Expression of stem cell markers is highly enriched in the CD117+SCA1+ subpopulations, which does not express committed progenitor or mature leukocyte markers. Besides CD44, expression of the adhesion molecules CD49d, CD49e, CD49f, CD54 and CD102 is high in HSPC. In comparison to unseparated BMC, only expression of the chemokine OPN and the cytokine/ chemokine receptors CD123, CD126, CD127 and Flt3 are increased in HSPC. BM-StrC differ from HSPC by frequently expressing several CD44v exon combinations, with high expression particularly of CD44v7 and CD44v10. BM-StrC do not express HSPC, committed progenitor or mature leukocyte markers. Expression of adhesion molecules is mostly lower than in HSPC, but expression of chemokines / cytokines frequently exceeds expression in HSPC.