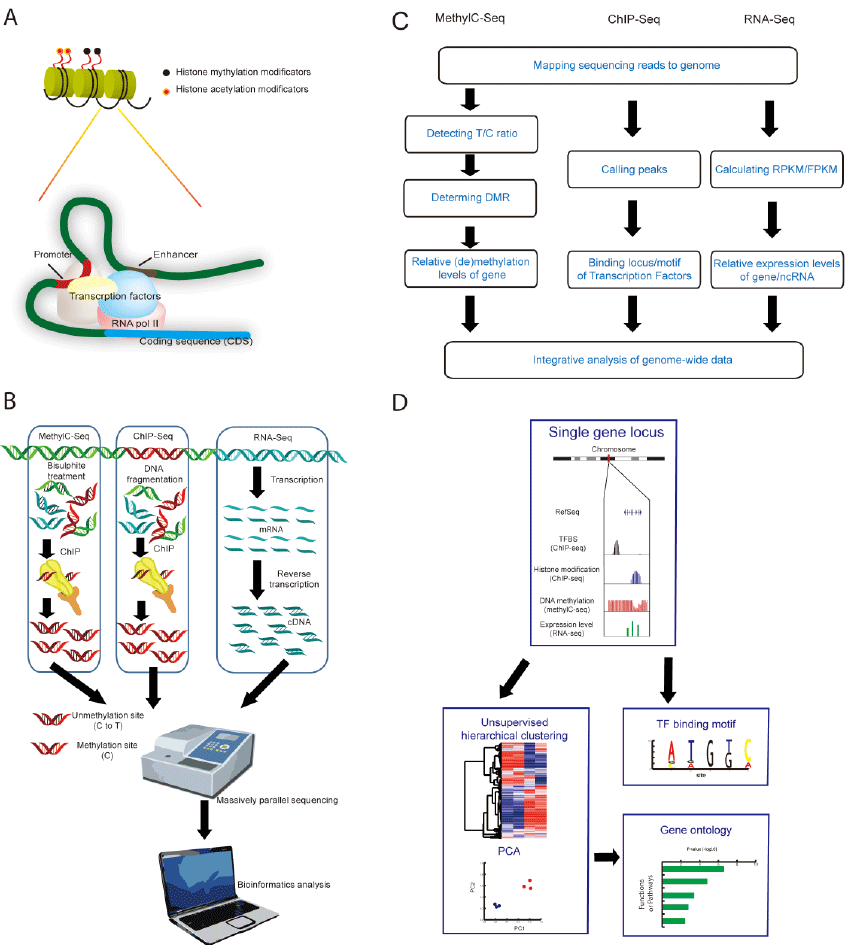
(A) Histone modifications and transcription regulations in ESCs. Histone modifications cause chromosome conformational arrangement. Transcription factors bind to promotor and enhancer regions. Histone modifications and transcription factors regulate gene expression co-orperatively. (B) Library constructions for genome wide massive sequencing. Genomic DNA are fragmented in ChIP-Seq, and bisulfite-treated in MethylC-Seq. Short DNA fragments which bind to target protein are pulled down by ChIP. In RNA-Seq, mRNA transcriptome are converted to cDNA library. Millions of short DNA readings in ChIP-Seq, RNA-Seq or MethylC-Seq library are sequenced in NGS platform, and are further analyzed using bioinformatics tools. (C) Workflow of bioinformatics processing; DMR: differentially methylated regions. (D) Integrative analysis of genome wide sequencing data. ChIP-Seq, RNA-Seq and MethylC-Seq data can be integrated at a single locus, and further analyzed systematically genome-wide by unsupervised hierarchical clustering, PCA, and gene ontology.