 |
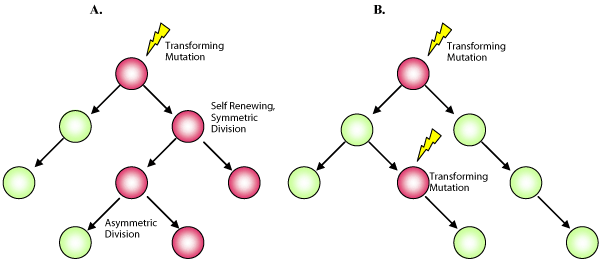
| Figure 1: Models of tumorigenesis: A. The cell-of-origin hypothesis; transforming mutations occur to a single cell which acquires or deregulates stem-like characteristics allowing it to divide symmetrically to self-renew or asymmetrically to generate differentiated cells in order to propagate and form a tumour. B. The clonal expansion hypothesis; transforming mutations occur to a number of cells during the process of tumorigenesis. |