 |
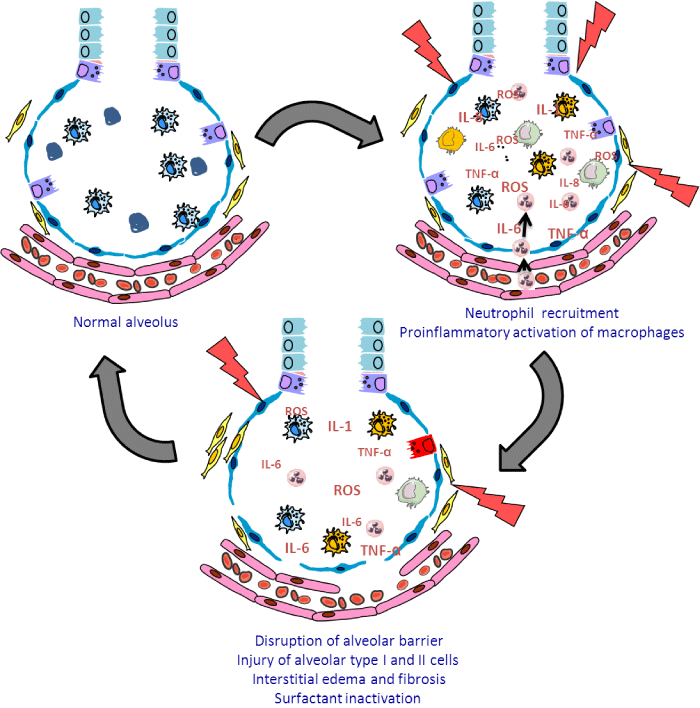
| Figure 1: Physiological basis of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Acute lung injury is characterized firstly by an increase in the neutrophil recruitment and the proinflammatory activation of macrophages. After that there is a disruption of the alveolar barrier, an injury of the alveolar cells and the marked increase in the volume of fluid and proteins leaving the vascular space, causing pulmonary edema. (ROS= Reactive Oxygen Species). |