 |
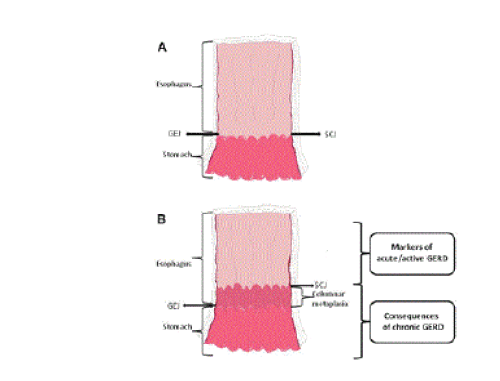
| Figure 1: The anatomy of the gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) and the squamocolumnar junction (SCJ) in GERD (modified from [12]). In normal individuals (A), the SCJ is located directly at the proximal margin of the gastric folds which corresponds to the anatomic GEJ. In patients with GERD (B), the SCJ may become displaced proximally due to columnar metaplasia of the distal esophagus. Changes related to acute and/or active GERD are diagnosed in squamous epithelium sampled from the distal esophagus, while the chronic consequences of GERD are present in biopsies sampled immediately below the SCJ. |