 |
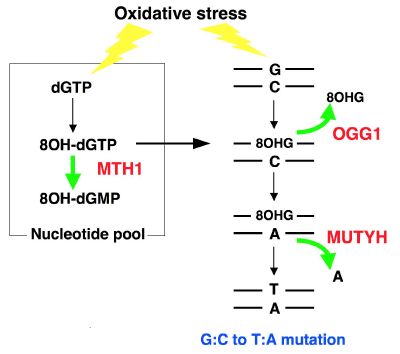
| Figure 1: Pathways for the removal of 8-hydroxyguanine (8OHG) in human cells. Oxidative stress causes the formation of 8OHG in DNA and 8-hydroxydGTP (8OH-dGTP) in the nucleotide pool. 8OHG paired with cytosine (C) is removed by OGG1 and adenine (A) paired with 8OHG is removed by MUTYH. If the 8OHG:A is not repaired, A pairs with thymine (T) in the next round of replication, thus leading to a G:C to T:A transversion mutation. 8OH-dGTP in a nucleotide pool is hydrolyzed to a monophosphate form by MTH1 so that the 8OH-dGTP can not be misincorporated into DNA. |