 |
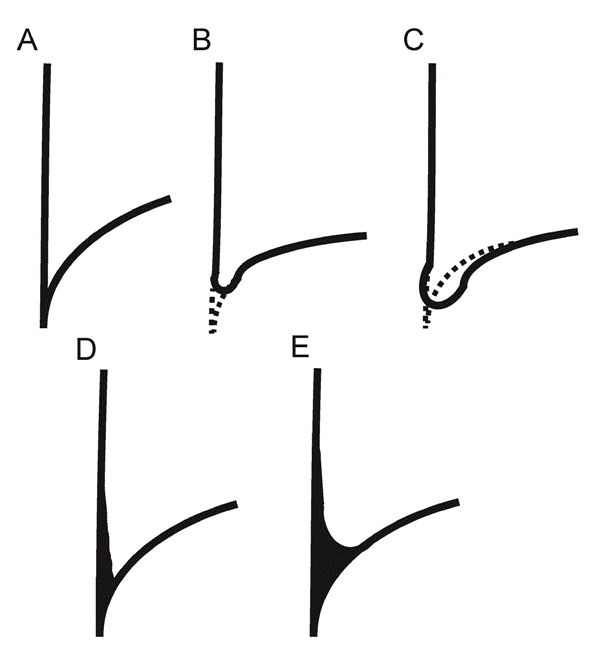
| Figure 4: Schematic diagrams of the costophrenic angle. A, normal CP angle, defined as a case in which the costal and diaphragmatic lines intersect at one point; B and C, blunt CP angle, defined in this study as convergence of the costal and diaphragmatic lines at a less acute angle (B) or a balloon shape (C) without medial displacement of the CP angle; D, displacement of the CP angle from the inner curve of the rib, an early sign of pleural effusion; E, blunt CP angle due to pleural effusion, which is accompanied by medial displacement of the CP angle. |