 |
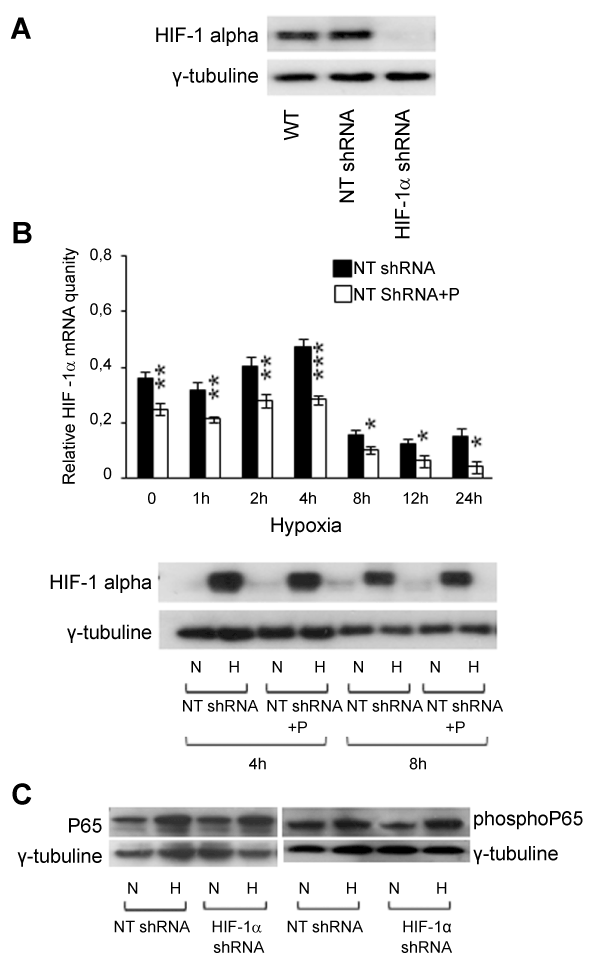
| Figure 3: Reciprocal modulation between HIF-1 alpha and NF-κB. (A) Nuclear HIF-1 alpha expression in wt MSTO, in a mix of MSTO clones transfected with non-targeting shRNA control vectors (NT shRNA) and in a mix of MSTO clones κnocκdown for HIF-1 alpha (HIF-1α shRNA) was detected by Western Blot at 4 hours of hypoxic treatment. γ-tubuline was used as loading control. A representative experiment is shown. (B upper panel) The effect of parthenolide (P) on HIF-1 alpha mRNA expression levels was detected in NT shRNA clones in normoxia and at different times of hypoxia by RT PCR. Values represent the mean ± SE of three different experiments. 18S rRNA was used as houseκeeping gene. NT shRNA + P vs NT sh RNA: *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001. (B bottom panel) The effect of parthenolide (P) on HIF-1 alpha nuclear protein expression was analyzed in NT shRNA clones by Western Blot in normoxia (N) and at 4 and 8 hours of hypoxia (H). γ-tubuline was used as loading control. A representative experiment is shown. (C) The effect of HIF-1 alpha silencing on NF-κB P65 (on the left) and phosphorylated NF-κB P65 (Ser276) (on the right) protein was detected by Western Blot. NT shRNA and HIF-1α shRNA clones were maintained in normoxic (N) or hypoxic conditions (H) for 30 minutes. γ-tubuline was used as loading control. A representative experiment is shown for both NF-κB P65 and pospho NF-κB P65 (Ser276). |