 |
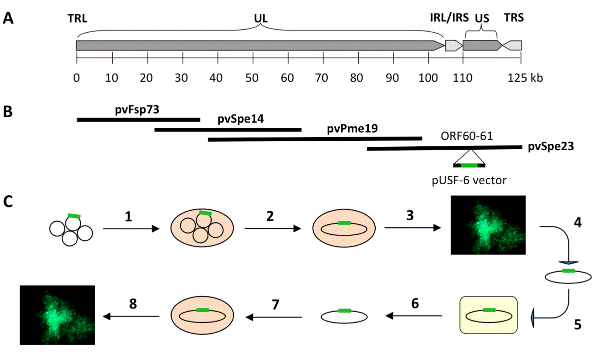
| Figure 1: Construction of VZV BAC. A. Schematic diagram of the VZV p-Oka genome. Image adapted from Zhang et al. [10]. B. Four cosmids containing overlapping VZV genomic segments are shown. A BAC vector (pUSF-6, shown in green) was inserted between ORF60 and ORF61 in VZV cosmid pvSpe23 by homologous recombination. Image adapted from Zhang et al. [10]. C. All four VZV cosmids were transfected into MeWo cells (1), and upon multiple successful homologous recombination events (2), the resulting recombinant virus was able to replicate and produced a green fluorescent plaque (3). The VZV BAC DNA was extracted from the cells (4) and transformed into electrocompetent DY380 E. coli in the presence of chloramphenicol (5). The infectivity of the recombinant BAC is tested by extraction from the E. coli (6) and transfecting it into human MeWo cells (7). The VZV BAC produced GFP-expressing virus that formed plaques (8). |