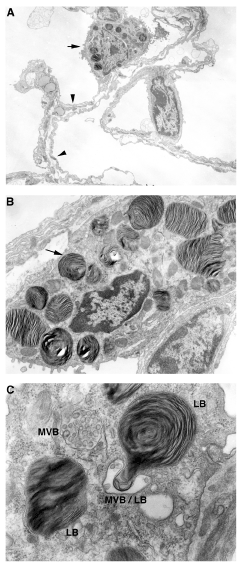
A: The alveolar surface is line by an epithelium of two distinct differentiated cell populations. A small set of cuboidal type II epithelial cells (arrow) produce and secrete surfactant onto the alveolar lumen, note surface microvilli and perinuclear granules. The surfactant film confers alveolar stability during respiratory cycles and prevents injury to the thin extended type I epithelial cells (arrowheads).
B: Higher magnification image of a type II cell. The type II cell is the singular site of SP-C synthesis. The mature type II cell contains numerous cytoplasmic lamellar bodies (arrow) formed by concentric lipid sheets. Lamellar bodies are the mature stored surfactant secretory granules.
C: High magnification depicts maturation of the lamellar body. Pre-lamellar multivesicular body (MVB) contains small membrane bound vesicles that fuse to form the lamellar body. MVB/LB indicates a transition structure of MVB partially incorporated into the growing lamellar body (LB) via continuous outer limiting membrane and internal vesicle-to-lamellar membranes. SP-C has been localized to the MVB and LB [11]. Magnifications: A: 2,700XB: 8,000XC: 27,000X Micrographs courtesy of Dr. Cheng-Lun Na.