 |
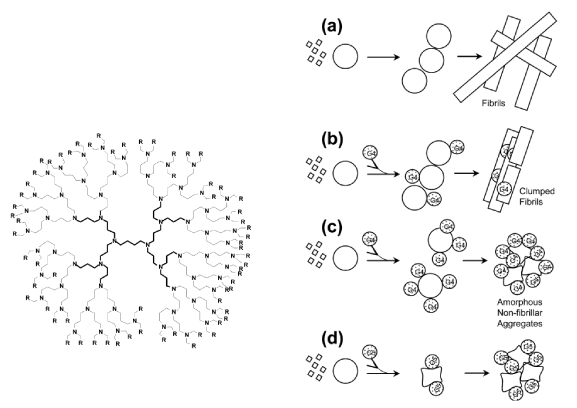
| Figure 5: Structure and function of PPI- Mal dendrimers.(A) Chemical structure of PPI-G4-Mal dendrimer. (B) Schematic representation of different dendrimer−amyloid interactions, and morphology of the resulting aggregated species (a) Polymerization process of Aβ(1−40): monomeric peptide (◇) assembles as peptide oligomers (O); peptide oligomers combine into prefibrillar structure (OOO) and eventually convert into fibrils (□□). (b) At low dendrimer-peptide ratios, the interaction of the PPI-G4-Mal dendrimer with the monomeric peptide does not prevent the fibrillization, but clumps fibrils. (c) at high dendrimer−peptide ratios, PPI-G4-Mal prevent the fibrillization leading to the formation of dendrimer−peptide oligomer complexes. These complexes combine in the form of granular nonfibrillar amorphous aggregates. (d) PPI-G5-Mal changes the peptide oligomeric structures, probably through formation of a higher number of hydrogen bonds per dendrimer. (even at low dendrimer−peptide ratios), thus preventing the fibrillization and leading to the formation of amorphous aggregates [36]. |