 |
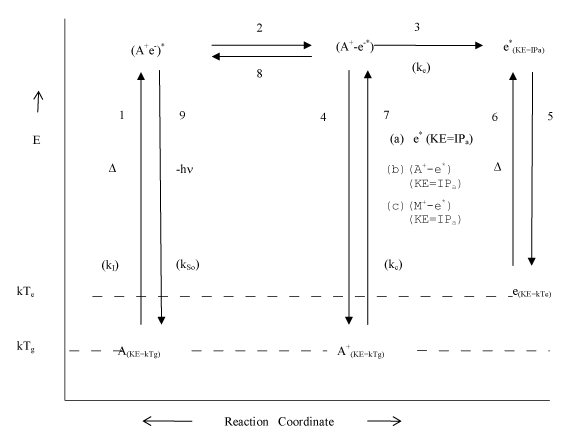
| Figure 3: Proposed detailed mechanism of thermal ionization and collisional radiative recombination involving (a) free electrons, (b) analyte ambipolar diffusion ion-electron pair complexes, and (c) interferent ambipolar diffusion ion-electron pair complexes (A, M and e denote analyte, interferent and electron respectively; (A+-e-)* denotes analyte ionization limit ion-electron complex, with electron held in the ionization limit atomic orbital; (A+-e*) = ambipolar diffusion ion-electron pair complex, with ionization energy centered on the electron; IPa=ionization potential of the analyte; Tg and Te denote kinetic gas temperature and electron temperature respectively; k=Boltzmann constant; KE = kinetic energy; kI, kSo, kc denote rate constants for ionization, radiative relaxation to the ground state, and collisional interaction; ke=rate constant for the release of the electron from the ambipolar diffusion ion-electron pair complex). (Source: [63]). |