 |
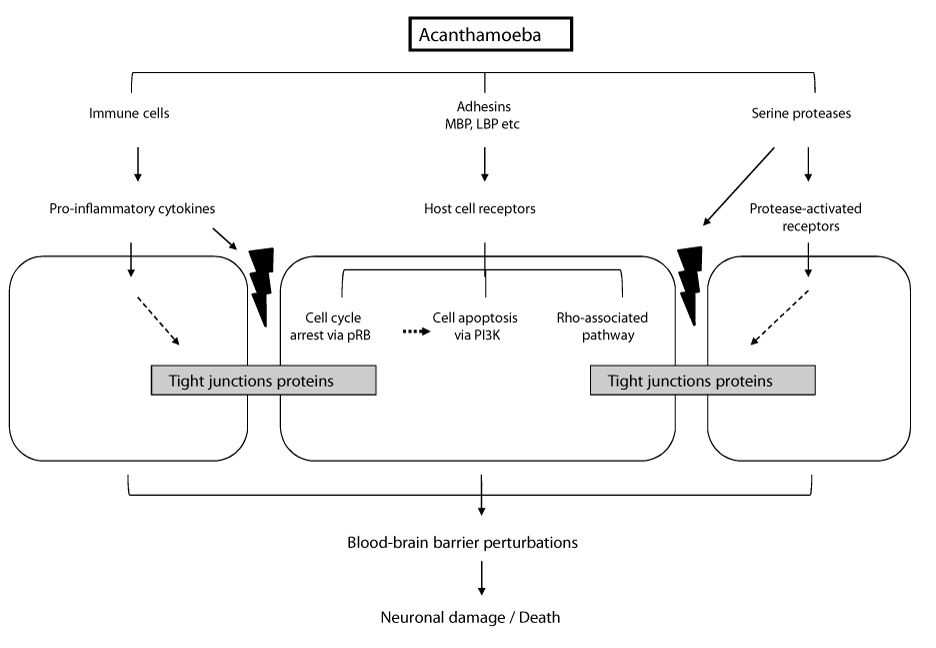
| Figure 4: Schematic illustration of Acanthamoeba interactions with the brain microvascular endothelial cells at the molecular-level. Acanthamoeba binds to host cells via mannose-binding protein (MBP), and possibly laminin-binding protein (LBP), which leads to cytoskeletal rearrangements involving Rho-associated pathways and host cell cycle arrest/apoptosis. Acanthamoeba secrete serine proteases that target tight junction proteins (zonula occludens and occludin) in a Rho kinasedependent manner. Both parasite and immune cell factors contribute to brain microvascular endothelial cell damage leading to Acanthamoeba entry into the brain. |