Volume 2
Environment Pollution and Climate Change
ISSN: 2573-458X
Climate Change 2018 &
Global ENVITOX 2018
October 04-06, 2018
Page 39
conference
series
.com
October 04-06, 2018
London, UK
16
th
Annual Meeting on
Environmental Toxicology and Biological Systems
&
5
th
World Conference on
Climate Change
JOINT EVENT
Manuela Marcoli, Environ Pollut Climate Change 2018, Volume 2
DOI: 10.4172/2573-458X-C1-001
Functional neuron-specific endpoints for
in vitro
neurotoxicity testing
Statement of the Problem:
In accordance with 3Rs, alternative models are required to replace standard neurotoxicity testing. High-
content, high-throughput tools are needed considering specific features of nervous system (NS) functioning to identify neurotoxic
vs. cytotoxic effects. By considering intercellular communication through transmitters and transmitter sensors (receptors), and
collective behavior of neuron network as relevant NS functional features, the purpose of this study is to develop tools providing
neuron-specific endpoints.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation:
A multi-disciplinary electrophysiological, neurochemical and immunocytochemical
approach, combining electrical activity recording of neuron network (on engineered micro-electrode arrays (MEAs) equipped with
60 electrodes onto which cerebrocortical neurons were cultured; data analysis through a home-made software and measurement of
transmitter release was used to assess network maturation and to detect effectiveness of neuroactive/neurotoxic substances.
Findings:
During network development, maturation of glutamatergic/GABAergic neuron networks, target for relevant neurotoxicity
mechanisms (excitotoxicity) and drugs classes, was observed. In mature networks, synaptic connectivity was related to activation
of glutamatergic pathways, and the system behaved as a sensitive sensor of glutamatergic transmission functioning. Activation or
blockade of NMDA/AMPA receptors, or blockade of glutamate transporters, induced firing and bursting activity variations related
to the effects on transmitter release. Also, the network sensed the fine transmission variations involved in synapse plasticity: the
collective network behavior and glutamate release were controlled by NMDA-dependent NO-cGMP pathway, as indicated by its
pharmacologicalmanipulation (NOsynthase/guanylyl cyclase inhibitors,NOdonors/8Br-cGMP). Bypresenting examples of network
activity modulation by neuroactive substances (glutamate/GABA receptor agonists/antagonists) and by known neurotoxicants
(e.g., domoic acid, chlorpyrifos oxon), and ineffectiveness of molecules not exhibiting acute neurotoxic effects, we report evidence
that MEAs-coupled neuron networks can represent an integrated approach for neurotoxicity testing based on functional neuron-
specific endpoints. They might provide an effective
in vitro
alternative tool for evaluating substance neurotoxicity, also providing a
mechanistic approach.
Manuela Marcoli
University of Genova, Italy
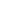
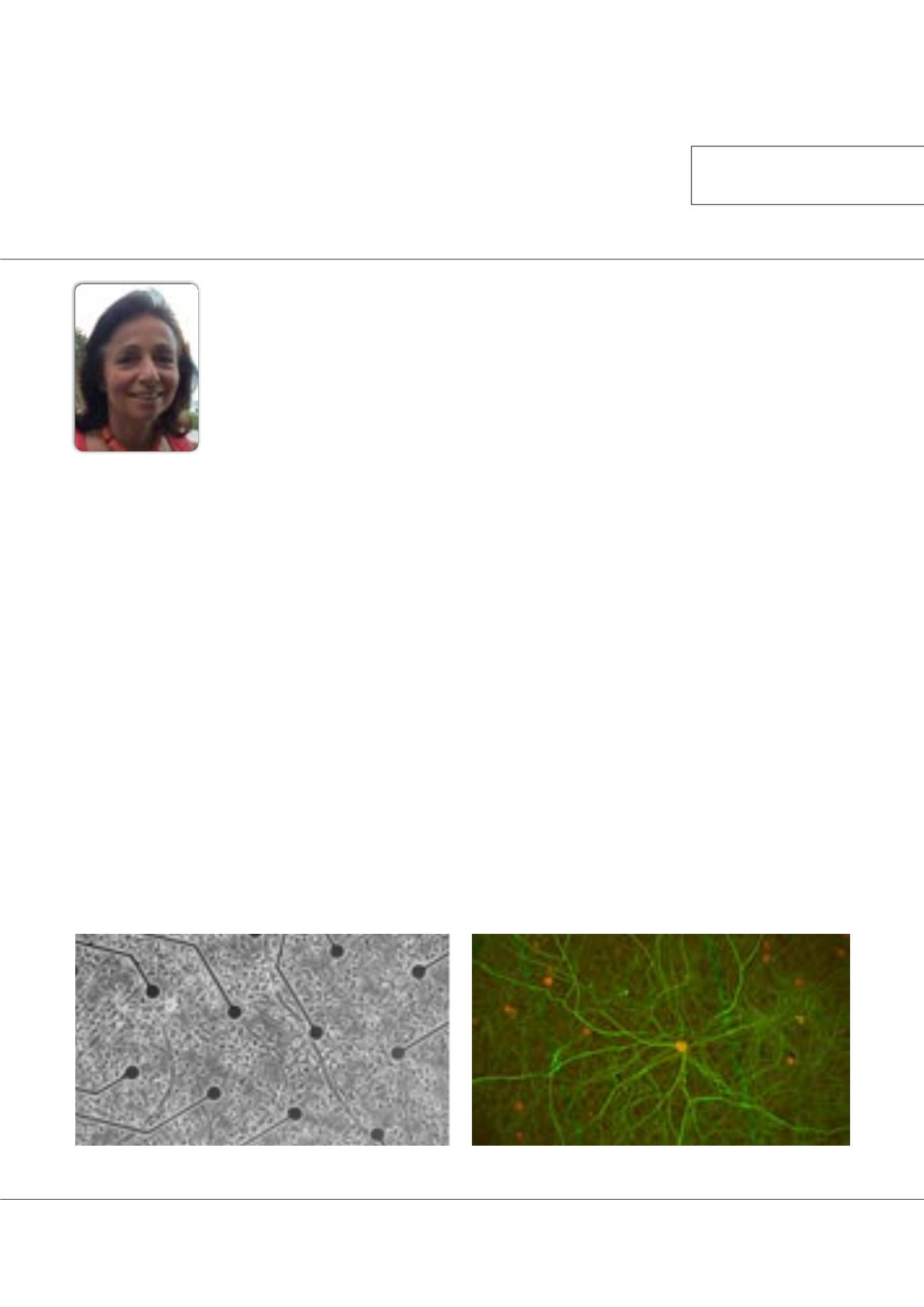
Figure 1:
Neuron network on MEAs; primary rat cerebrocortical neuron cultures from E19, 24 DIV. The network on microelectrode arrays is shown.
Immunocytochemistry for MAP2 (green) and NeuN (red).