Volume 7
Biosensors Journal
ISSN: 2090-4967
Electrochemistry 2018
June 11-12, 2018
Page 40
conference
series
.com
June 11-12, 2018 | Rome, Italy
4
th
International Conference on
Electrochemistry
W Knoll, Biosens J 2018, Volume 7
DOI: 10.4172/2090-4967-C1-001
Polyelectrolyte multilayer assemblies and brushes on reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistors
for sensing applications
G
raphene, a two-dimensional zero band gap semiconducting material, has gained considerable interest in material science,
energy storage and sensor technology, due to its remarkable electronic and mechanical properties. It’s high carrier mobility
and ambipolar field effect, together with a great sensitivity towards changes in environmental conditions makes graphene perfectly
suitable as transducing material for the use in various types of sensors. In this report, we first describe a novel biosensor exploiting
the pH dependence of liquid gated graphene-based field-effect transistors for the enzymatic detection of urea. The channel between
the interdigitated source-drain microelectrodes was non-covalently functionalized with bilayers of poly (ethylene imine) and urease
using the layer-by-layer approach, providing a LoD below 1 μM urea. Next, we present a sensor based on a reduced graphene oxide
field effect transistor (rGO-FET) functionalized with the cascading enzymes arginase and urease as recognition elements in a layer
by layer assembly with poly (ethylene imine). The build-up of this nano-architecture was monitored by surface plasmon resonance
spectroscopy. L-arginine was quantitatively detected by the change in current between source and drain electrode due to electrostatic
gating effects conferred by the formation of OH
-
ions upon enzymatic hydrolysis of the analyte L-arginine. And finally, we will
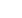
describe first results on the coupling of calcium-responsive polymer brushes to graphene field-effect transistors. The presence of Ca
+2
ions neutralize the charge of the phosphate groups leading to a change of the Dirac point by electrostatic gating effects. A formalism
using the Langmuir adsorption model and the Grahame equation is used to obtain the surface coverage from the change of the Dirac
point.
Figure 1:
Coupling calcium-responsive polymer brushes to graphene field-effect transistors.
Recent Publications
1. Berninger T, Bliem C, Piccinini E, Azzaroni O and Wolfgang Knoll W (2018) Cascading reaction of arginase and urease
on a graphene-based FET for ultrasensitive, real-time detection of arginine. Biosens. Bioelectron.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.05.027.
2. Piccinini E, Alberti S, Longo G, Berninger T, Breu J, Dostalek J, Azzaroni O and Knoll W (2018) Pushing the boundaries of
interfacial sensitivity in graphene FET sensors: polyelectrolyte multilayers strongly increase the Debye screening length. J.
Phys. Chem. 122(18):10181–10188
WKnoll
Austrian Institute of Technology, Austria