Page 64
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8
International Journal of Waste Resources
ISSN: 2252-5211
Recycling Expo 2018
June 25-26, 2018
June 25-26, 2018 | Berlin, Germany
8
th
World Congress and Expo on Recycling
Removal of Pb
2+
, Ni
2+
, Cd
2+
, Zn
2+
from wet process phosphoric acid by mueroxide impregnated
activated bentonite
Mohamed F Cheira
1
, Mohamed N Rashed
2
, Adila E Mohamed
2
and
Mohamed A Awadallah
2
1
Nuclear Materials Authority, Egypt
2
Aswan University, Egypt
T
he harmful inorganic impurities in wet process phosphoric acid are essentially removed by a simple and inexpensive
method for environment applications. In this work, the highly efficient removal of Pb
2+
, Ni
2+
, Cd
2+
and Zn
2+
cations (
>99%) from WPPA were investigated through a batch technique using mueroxide impregnated activated bentonite. The
used adsorbent was prepared within a dry method. The experimental data showed high adsorption capacity of mueroxide
impregnated activated bentonite toward Pb
2+
, Ni
2+
, Cd
2+
, and Zn
2+
cations into its active sites as 170, 115, 143 and 190 mg/g at
5 M acid concentration, respectively. Moreover, most of the heavy metals were completely adsorbed from WPPA (>98%) at 5
M acid concentration. The providing data indicated that the batch sorption technique retained its functionality to effectively
remove Pb
2+
, Ni
2+
, Cd
2+
and Zn
2+
cations even after six reuse/cycles, where the mueroxide impregnated activated bentonite can
be regenerated using HCl. The real impurities removal from the Abu Zabaal wet process phosphoric acid using the adsorbent
was assessed through the proposed protocol under optimum conditions.
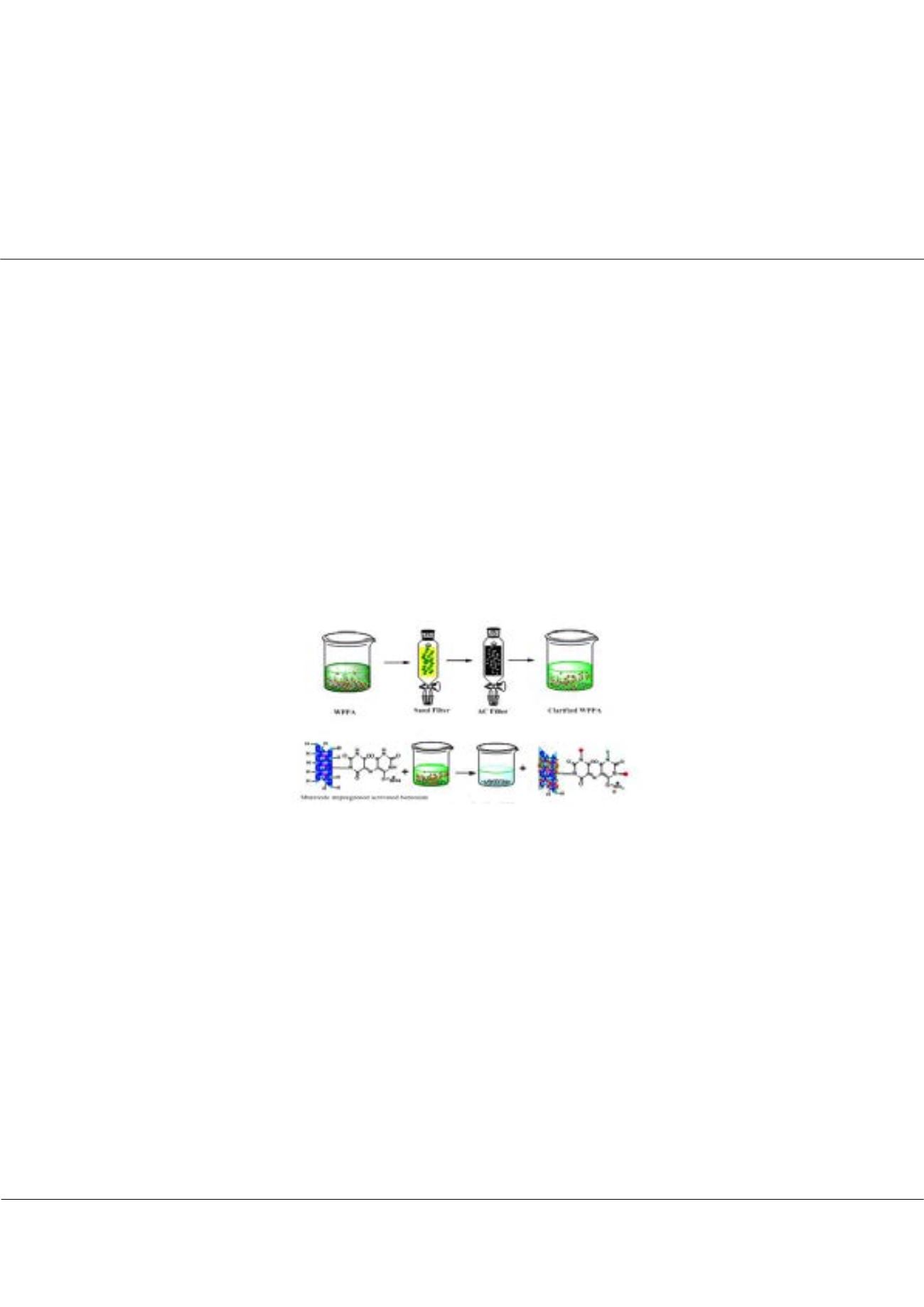
Figure 1:
Mechanism of removal of metal ions impurities from WPPA using mueroxide impregnated activated bentonite.
Recent Publications
1. Cheira M F (2015) Characteristics of uranium recovery from phosphoric acid by an aminophosphonic resin and
application to wet process phosphoric acid. European Journal of Chemistry 6(1):48‐56.
2. Cheira M F, Zidan I H and Manaa E A (2014) Potentiality of white sand for the purification of wet process phosphoric
acid from some metallic elements (U, Zn, Cd). Chemical Technology 9(6):224-233.
3. Abdien H G, Cheira M F, Abd-ElraheemMA, Saef El Naser T A and Zidan I H (2016) Extraction and pre-concentration
of uranium using activated carbon impregnated trioctyl phosphine oxide. Applied Chemistry 100:43462-43469.
4. Gomaa H, Shenashen MA, Yamaguchi H, Alamoudi A S, Abdelmottaleb M , Cheira M F, Seaf El-Naser T A and El-Safty
S A (2018) Highly-efficient removal of AsV, Pb
2+
, Fe
3+
and Al
3+
pollutants fromwater using hierarchical, microscopic TiO
2
and TiOF
2
adsorbents through batch and fixed-bed columnar techniques. Journal of Cleaner Production 182:910-925.
5. Al-Harahsheh M, Hussain Y A, Al-Zoubi H, Batiha M and Hammouri E (2017) Hybrid precipitation-nanofiltration
treatment of effluent pond water from phosphoric acid industry. Desalination 406:88–97.
Mohamed F Cheira et al., Int J Waste Resour 2018, Volume 8
DOI: 10.4172/2252-5211-C1-011