Page 50
Notes:
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 3, Issue 1 (Suppl)
Toxicol Open Access
ISSN: 2476-2067 TYOA, an open access journal
Toxicology Congress 2017
April 13-15, 2017
April 13-15, 2017 Dubai, UAE
8
th
World Congress on
Toxicology and Pharmacology
Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and its monohydroxilated metabolites in human liver
cells using gas chromatography and high performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry
Vincent Lal
1
, Cheng Peng
1
, Mary T Fletcher
1
, Stephen T Were
2
and
Jack C Ng
1
1
The University of Queensland, Australia
2
Biosecurity Queensland, Australia
H
uman cell-based models can provide important information on exposure and risk from chemical contaminants.
Measurement of the amount of chemical contaminant entering the cells and how effectively it is metabolised and removed
can be useful towards our understanding of chemical health risk assessment.
The aim for our study is to quantify intracellular uptake and metabolism of
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a human liver carcinoma cell
line (HepG2 cells) exposed to environmentally relevant concentrations of
the pure model compound and contaminated soils. A number of PAH and
their monohydroxilated metabolites, including 3-hydroxybenzo[a]pyrene,
1-naphthol and 1-hydroxypyrene were found in human liver cells following
exposure. Biotransformation of PAHs in human liver cells increased with
increasing dose. Cell exposure close to 0 h and to 24 h contact times was also
investigated, both at low and high dosage. Benzo[a]pyrene was found to be toxic
to cells; however, remaining PAHs in this study did not cause any significant
changes in cell viability (or cytotoxicity) and their ability to recover. Chemical
characterisation of PAHs and its metabolites was done using high performance
liquid chromatography coupled to a high resolution mass spectrometer (HPLC-
HRMS) and gas chromatography with mass spectrometry (GCMS). The ability
to quantify chemical uptake and fate using human cell line based models will
contribute to a more refined chemical risk assessment.
Recent Publications
• Peng C, Muthusamy S, Xia Q, Lal V, Denison M S and Ng J C (2015) Micronucleus formation by single and mixed heavy
metals/loids and PAH compounds in HepG2 cells. Mutagenesis. 30 (5): 593-602.
Biography
Vincent Lal has his expertise in Environmental and Analytical Toxicology and passion in improving human health and wellbeing. His work is based on chemical
risk assessment using
in vitro
technologies. He has several years of research, teaching, consultancy and administration experience in commercial and education
institutions.
v.lal3@uq.edu.auVincent Lal et al., Toxicol Open Access 2017, 3:1 (Suppl)
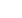
http://dx.doi.org/10.4172/2476-2067.C1.002Figure 1:
Quantification of PAHs uptake
and metabolism in human liver cells
(HepG2) using Gas Chromatography
and Liquid Chromatography with Mass
Spectrometry