Page 33
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8, Issue 4 (Suppl)
J Pet Environ Biotechnol, an open access journal
ISSN: 2157-7463
Oil Gas Expo 2017
July 13-14, 2017
Oil and Gas
July 13-14, 2017 Berlin, Germany
3
rd
International Conference and Expo on
Characterization of oil-water two-phase flow based on terahertz time-domain spectroscopy
Yan Song
and
Hong L Zhan
China University of Petroleum, China
U
nderstanding the dynamics behaviors of oil-water two-phase flow is crucial to important problems in the oil wells and pipelines.
Because of the extremely high sensitivity of terahertz wave to hydrogen bonding, a new method to study oil-water two-phase
flow is put forward using the terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS). By comparing the amplitudes of the maximum peak in
THz-TDS, the ability of THz-TDS has been shown previously to discriminate the flow pattern for oil-water two-phase flow with low
water content in rectangular pipe. For further study on oil-water two-phase flow, we conduct another experiment using diesel and tap
water. The amplitude of THz-TDS of oil-water two-phase flow is corresponding to the flow pattern, the flow pattern and the critical
flow rate can be distinguished by THz-TDS. When the oil-water mixture flow rates are high, the water phase is intensively impacted
by the oil phase and W/O flow is found and the water content in the test part almost keeps unchanged in this situation resulting in the
unchanged THz signal in the measurement. As the decrease of mixture flow rate, the droplets are mainly affected by gravity and the
force associated with the motion reduces. For further decrease in the mixture flow velocities, the number of droplets reduces and the
maximum drop size increases, the flow is gravity dominated and then the O and DW/O flow pattern is formed. In order to investigate
the effect of the input mixture flow rate on the slip, simulations have been performed under selected mixture flow rates for the two-
phase flows with different input water fractions. The results reveal that the slip is mainly dominated by the mixing flow rate at low flow
rates, whereas the effect decreases gradually with increasing flow rate.
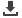
Figure 1:
Critical flow rate
Q
c
and Reynolds number for different input water volume fractions diesel oil-water two phase flows. The
inserts present sketches of the flow patterns: an oil layer over a dispersion of water in oil flow (O and DW/O) and an emulsion of
water in oil flow (W/O).
Biography
Yan Song has her expertise in the evaluation and characterization of fluid (microfluidic) flow in the oil and gas field based on new optical method. Her research of
oil-water two-phase flow based on terahertz time-domain spectroscopy makes supplement of flow pattern analysis in the oil and gas field.
1564191660@qql.comYan Song et al., J Pet Environ Biotechnol 2017, 8:4 (Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2157-7463-C1-034