Quantum Physics, Optics and
Laser Technologies
Page 21
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 5
Journal of Lasers, Optics & Photonics
Physicists Congress 2018
May 09-10, 2018
May 09-10, 2018 Tokyo, Japan
International Conference on
MID-IR spectroscopy of Nd
3
+ and Ce
3
+ ions in crystals
Alessandra Toncelli, Jihua Xu and Alessandro Tredicucci
University of Pisa, Italy
T
he mid-infrared (MID-IR) region is very interesting for a large number
of applications because vibro-rotational levels of many molecules lie in
this region. Therefore, the search for new light sources in this range is a very
important research topic. Moreover, MID-IR energy levels of rare earth ions
in crystals are usually the bottom laser levels for visible or near infrared lasers
based on these materials. For these reasons, we performedMID-IR spectroscopy
of the Nd
3+
-Ce
3+
:YAG system. Ce
3+
ions are added as sensitizers for Nd
3+
because
Ce
3+
possesses a strong absorption band at around 450 nm where powerful
diode lasers exist. The efficient energy transfer mechanism at visible energy that
transfers the Ce excitation to the upper Nd laser level has already been studied,
but, at the best of our knowledge, no detailed investigation has been performed
about the possible interaction between the MID-IR energy levels of the two ions.
This might play an important role in the laser efficiency because of the possible
energy match with the bottom laser level of the near-infrared Nd emission.
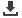
Absorption spectra of Nd:YAG, Ce:YAG and Nd,Ce:YAG have been performed as a function of temperature in the 7000-1000
cm
-1
wavenumber range to identify the transparency limit of the crystal matrix and the MID-IR energy levels of the two ions.
Ce:
2
F
7/2
together with Nd:
4
I
15/2
,
4
I
13/2
and
4
I
11/2
Stark sublevels have been observed and identified. Good spectral overlap has been
observed between the Ce:
2
F
7/2
Stark components and Nd:
4
I
13/2
, and
4
I
11/2
multiplets. This might help in depopulating the lower
laser level of the 1.06µm and 1.3 µm laser emission of Nd thus favoring the laser emission at these wavelengths. Moreover, the
4.8-5 µm Nd emission has been observed and characterized at room temperature.
Recent Publications
1. R Marino, I Lorgeré, O Guillot-Noël, H Vezin, A Toncelli, M Tonelli, J-L LeGouët, P Goldner (2016) Energy level structure
and optical dephasing under magnetic field in Er
3+
:LiYF
4
at 1.5 μm.
J. Lumin.
; 169: 478-482.
2. N Hamza Belkhir, A Toncelli, Abdul K Parchur, E Alves, R Maalej (2017) Efficient temperature sensing using
photoluminescence of Er/Ybimplanted GaN thin films.
Sensors and Actuators B
; 248: 769–776.
Biography
Alessandra Toncelli has obtained her PhD in Physics in 1998 at the University of Pisa. Since 2017 she is Associate Professor at the Physics Department of Pisa.
Her scientific interest was initially aimed to the growth and spectroscopy of crystalline materials for photonic applications in visible and near infrared regions. In
particular, she studied and characterized the optical and spectroscopic properties of oxide and fluoride crystals with rare earths for laser applications. She has
published more than 160 articles on International journals. She currently holds an h-index of 41 both in Scopus and in ISI web of knowledge.
alessandra.toncelli@unipi.itAlessandra Toncelli et al., J Laser Opt Photonics 2018, Volume 5
DOI: 10.4172/2469-410X-C1-020
7000
6000
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
1
2
3
4 5 6 7 8910
Ce:
2
F
7/2
Transparency limit
Nd:
4
I
15/2
Nd:
4
I
13/2
Nd:
4
I
11/2
Abs(cm
-1
)
Wavenumber(cm
-1
)
Nd:YAG
Ce:YAG
Wavelength (
µ
m)