Page 102
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 6, Issue 4 (Suppl)
Agrotechnology, an open access journal
ISSN: 2168-9881
Agri 2017
October 02-04, 2017
allied
academies
10
th
International Conference on
AGRICULTURE & HORTICULTURE
October 02-04, 2017 London, UK
Market evolution of garlic (
Allium sativum
L.) in Argentina (
Ex aecquo
)
Ana María Castagnino
1
, Karina E Diaz
1
, Sabrina Mondini
1
, W John Rogers
1
, Andrea Guisolis
1
, Oscar Liverotti
2
, José Fernandez Lozano
3
and
Mario E
Peralta
4
1
UNCPBA, Argentina
2
Pontifical Catholic University of Argentina, Argentina
3
University of Buenos Aires, Argentina
4
University of Belgrano, Argentina
G
arlic is one of themost economically, productively and socially important horticultural products in Argentina, valued for its
nutraceutical, bacteriostatic, fungistatic and antioxidant properties, amongst others. It is commercialized mainly in fresh
form for both the internal market and exportation, in which Argentina occupies second place (behind China). Exportation is
concentrated into three months, whereas the internal market operates all year, represented by several types of variety in distinct
provinces. With the aim of analyzing garlic market evolution in Argentina based upon the volume received by the Buenos Aires
Central Market, the following aspects were evaluated: total commercial volumes 2002-2016, type of varieties commercialized
over the study period (TV) and province of origin commercialized in 2016. From comparative analysis between the first and
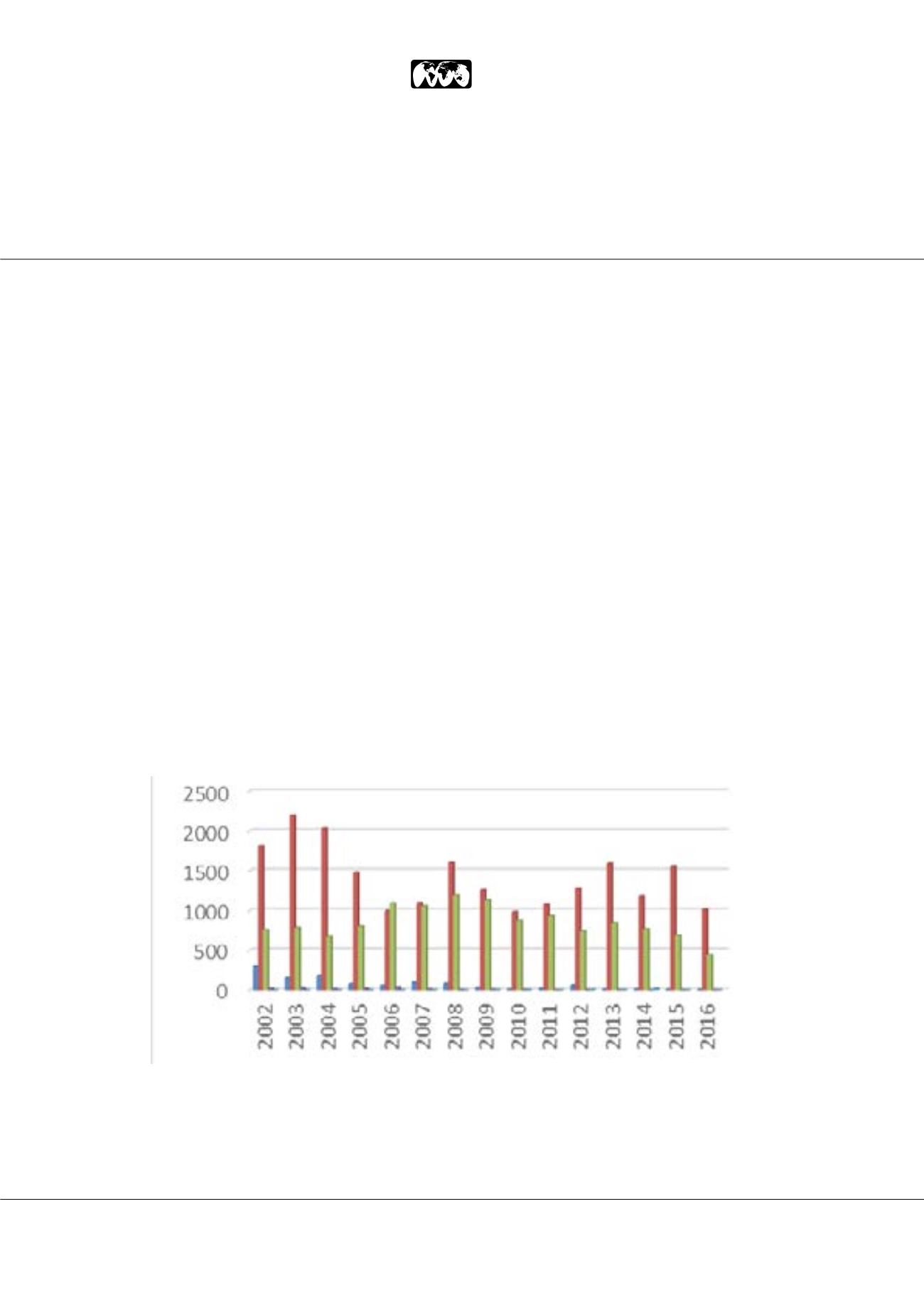
final years of the study, a decrease of 50% was observed (2002: 2902t and 2016: 1466t). The total volume commercialized in
the period was 35313t and the mean annual volume was 2354t, with the following exceeding the mean: 2003: by 35% (a) and
2004, 2002 and 2008: by 23% (ab), 2013: by 4% and 2009: by 3%. Garlic for the internal market was produced in nine provinces,
with 98.25% of the total commercial volume concentrated in three provinces: San Juan (33%), Mendoza (32.75%) and Buenos
Aires (32.5%), followed by Río Negro (0.72%), Corrientes (0.5%), Santa Fe (0.32%), Santiago del Estero (0.3%), Jujuy (0.2%)
and Tucumán (0.15%). Regarding TV for 2002-2016, 99.44% corresponded to three varieties: Colorado 60.03% (a), Chino
36.25% (b) and Blanco 3.16% (c), followed by Rosado 0.45% (c) and Ruso 0.11% (c). The results demonstrate the excessive
concentration of the offer in just a few provinces. Furthermore, they indicate the institutional necessity to promote increased
varietal diversification and expand the production and commercialization of the internal market of this highly beneficial
product for health.
Biography
Ana María Castagnino is a Horticulture Specialist (UNIPI, Italy) with a Master's Degree in Business Management (UNCPBA, Argentina), and is Professor of
Horticulture at UCA, Buenos Aires and Associate Professor at UNCPBA. She is a member of CRESCA (Regional Centre for the Systemic Study of Agro-Food
Chains) and directs the programme "Promotion of the production and consumption of asparagus and other non-traditional vegetables".
amc@hotmail.comAna María Castagnino et al., Agrotechnology 2017, 6:4(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2168-9881-C1-028