Page 91
conferenceseries
.com
Volume 8, Issue 9 (Suppl)
J Clin Exp Cardiolog, an open access journal
ISSN: 2155-9880
Euro Cardiology 2017
October 16-18, 2017
October 16-18, 2017 | Budapest, Hungary
20
th
European
Cardiology
Conference
Low-density lipoproteins and triglyceride removal by plasma perfusion with active charcoal at
atherosclerosis and cholestatic liver disease
Zarina R Khaybullina, Rustam A Sadykov, Olga V Kim
and
Lusia M Akhmedjanova
Republican Specialized Center of Surgery, Uzbekistan
Statement of the Problem:
The development of artificial organs support system remains an important issue due to a high
mortality rate of multi-organ dysfunction. Atherosclerosis and chronic cholestatic liver disease is common associated with
hyperlipidemia, increase of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol level. Active charcoal (AC), a highly porous material, has
been widely used for endotoxins reducing through hemoperfusion. Plasma perfusion has several advantages: less loss of blood
components, less activation of the coagulation system, safety. The purpose of this study is to evaluate adsorption capacity of AC
for total bilirubin (TBil), total cholesterol (TC), LDL, triglyceride (TG) and its removal.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation:
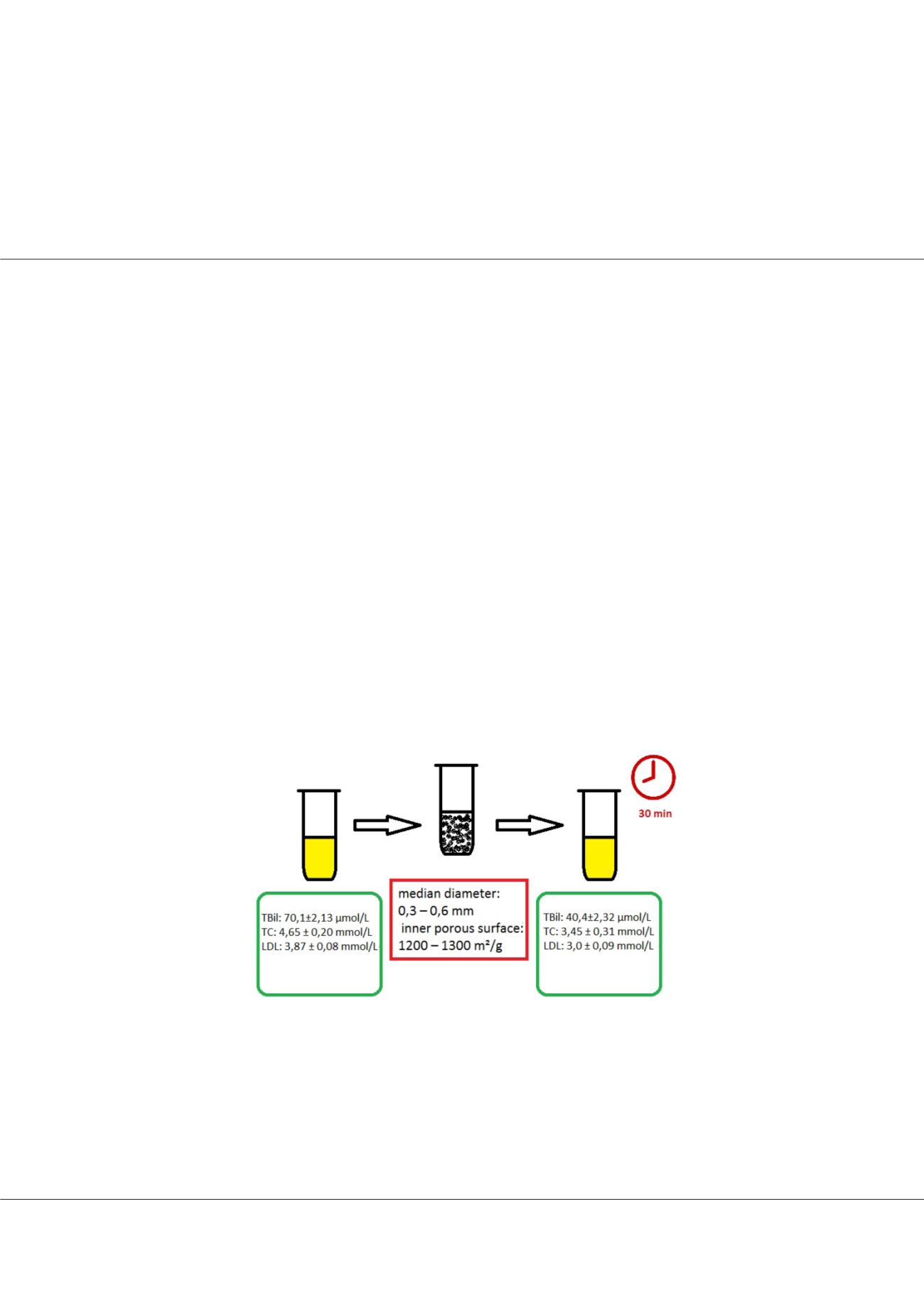
Static adsorption experiments
in vitro
was made using AC with median diameter
0.3–0.6 mm; the inner porous surface ranged between 1200–1300 m²/g. 350 mg AC have been washed with 5 ml normal saline
and then 1.0 ml of human plasma was added to AC in lab tube with diameter 1.5 cm. Adsorption lasted 30 min. Concentration
of TC, LDL, TG, TBil were made before and after adsorption with AC on the automatic analyzer «VITROS-350» (USA).
Statistical analysis was performed using Excel Microsoft for t-pair test. Significance was at the P<0.05 level.
Findings:
The results of the experiment
in vitro
demonstrate high adsorption capacity of AC during static plasma adsorption.
After plasma adsorption TBil decreased on 42.3%, TC – on 25.8%, LDL – on 22.48%, urea – on 49.7%%, creatinine – on 71.6%
(p<0.01).
Conclusion & Significance:
Plasma perfusion using AC may be used for the treatment of cholestatic liver failure disease and
decrease a risk of cardiovascular disease among these patients.
Biography
Zarina R Khaybullina has completed her PhD and Post-doctoral studies from Biochemistry institute of Academy of Science of Republic of Uzbekistan. She is the
Head of Biochemistry department at Republican Specialized Centre of surgery named after academician V. Vakhidov and Professor of Biochemistry department
at Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute. She has published more than 39 papers in reputed journals and has been serving as member of Scientific Council in
Biochemistry and Biophysics. Her research field includes “Free radical biology and medicine, biochemistry of antioxidants, ultra-low concentrations of biologically
active substances, biochemistry of atherosclerosis and metabolic syndrome”.
zrkhaybullina1@gmail.comZarina R Khaybullina et al., J Clin Exp Cardiolog 2017, 8:9(Suppl)
DOI: 10.4172/2155-9880-C1-078